Sex-Specific Genetic and Transcriptomic Liability to Neuroticism
- PMID: 36244801
- PMCID: PMC10508260
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2022.07.019
Sex-Specific Genetic and Transcriptomic Liability to Neuroticism
Abstract
Background: The presentation, etiology, and relative risk of psychiatric disorders are strongly influenced by biological sex. Neuroticism is a transdiagnostic feature of psychiatric disorders displaying prominent sex differences. We performed genome-wide association studies of neuroticism separately in males and females to identify sex-specific genetic and transcriptomic profiles.
Methods: Neuroticism scores were derived from the Eysenck Personality Inventory Neuroticism scale. Genome-wide association studies were performed in 145,669 females and 129,229 males from the UK Biobank considering autosomal and X chromosomal variation. Two-sided z tests were used to test for sex-specific effects of discovered loci, genetic correlates (n = 673 traits), tissue and gene transcriptomic profiles, and polygenic associations across health outcomes in the Vanderbilt University Biobank (39,692 females and 31,268 males).
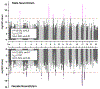
Results: The single nucleotide polymorphism heritability of neuroticism was not statistically different between males (h2 = 10.6%) and females (h2 = 11.85%). Four female-specific (rs10736549-CNTN5, rs6507056-ASXL3, rs2087182-MMS22L, and rs72995548-HSPB2) and 2 male-specific (rs10507274-MED13L and rs7984597) neuroticism risk loci reached genome-wide significance. Male- and female-specific neuroticism polygenic scores were most significantly associated with mood disorders (males: odds ratio = 1.11, p = 1.40 × 10-9; females: odds ratio = 1.14, p = 6.05 × 10-22). They also associated with sex-specific laboratory measurements related to erythrocyte count, distribution, and hemoglobin concentration. Gene expression variation in the pituitary was enriched for neuroticism loci in males (male: b = 0.026, p = .002), and genetically regulated transcriptomic changes highlighted the effect of SHISHA9, TEX26, and NCOA6.
Conclusions: Through a comprehensive assessment of genetic risk for neuroticism and the associated biological processes, this study identified several molecular pathways that can partially explain the known sex differences in neurotic symptoms and their psychiatric comorbidities.
Keywords: Biomarkers; GWAS; Neuroticism; Pituitary gland; Sex effects; TWAS.
Copyright © 2022 Society of Biological Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURES
Drs. Gelernter is named as an inventor on PCT patent application #15/878,640 entitled: “Genotype-guided dosing of opioid agonists,” filed January 24, 2018. Dr. Stein is paid for his editorial work on the journals Biological Psychiatry and Depression and Anxiety, and the health professional reference Up-To-Date; he has also in the past 3 years received consulting income from Actelion, Acadia Pharmaceuticals, Aptinyx, atai Life Sciences, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bionomics, BioXcel Therapeutics, Eisai, Clexio, EmpowerPharm, Engrail Therapeutics, GW Pharmaceuticals, Janssen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and Roche/Genentech. Drs. Polimanti and Gelernter are paid for their editorial work on the journal Complex Psychiatry. The other authors have no competing interests to report.
Dr. Krystal’s financial disclosures are as follows:
Consultant (Note: – The Individual Consultant Agreements listed below are less than $5,000 per year)
Aptinyx, Inc., Atai Life Sciences, Biogen, Idec, MA, Bionomics, Limited (Australia), Boehringer Ingelheim International, Cadent Therapeutics, Inc., Clexio Bioscience, Ltd., COMPASS Pathways, Limited, United Kingdom, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Epiodyne, Inc. , EpiVario, Inc., Greenwich Biosciences, Inc., Heptares Therapeutics, Limited (UK), Janssen Research & Development, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc., Perception Neuroscience Holdings, Inc. , Spring Care, Inc., Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Takeda Industries, Taisho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd
Board of Directors
Freedom Biosciences, Inc.
Scientific Advisory Board
Biohaven Pharmaceuticals, BioXcel Therapeutics, Inc. (Clinical Advisory Board), Cadent Therapeutics, Inc. (Clinical Advisory Board), Cerevel Therapeutics, LLC, Delix Therapeutics, Inc., EpiVario, Inc., Eisai, Inc., Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, PsychoGenics, Inc., Neumora Therapeutics, Inc. , Tempero Bio, Inc., Terran Biosciences, Inc.
Stock
Biohaven Pharmaceuticals , Sage Pharmaceuticals, Spring Care, Inc.
Stock Options
Biohaven Pharmaceuticals Medical Sciences , EpiVario, Inc., Neumora Therapeutics, Inc. , Terran Biosciences, Inc., Tempero Bio, Inc.
Income Greater than $10,000
Editorial Board
Editor - Biological Psychiatry
Patents and Inventions
1. Seibyl JP, Krystal JH, Charney DS. Dopamine and noradrenergic reuptake inhibitors in treatment of schizophrenia. US Patent #:5,447,948.September 5, 1995
2. Vladimir, Coric, Krystal, John H, Sanacora, Gerard – Glutamate Modulating Agents in the Treatment of Mental Disorders. US Patent No. 8,778,979 B2 Patent Issue Date: July 15, 2014. US Patent Application No. 15/695,164:
Filing Date: 09/05/2017
3. Charney D, Krystal JH, Manji H, Matthew S, Zarate C., - Intranasal Administration of Ketamine to Treat Depression United States Patent Number: 9592207, Issue date: 3/14/2017. Licensed to Janssen Research & Development
4. Zarate, C, Charney, DS, Manji, HK, Mathew, Sanjay J, Krystal, JH, Yale University “Methods for Treating Suicidal Ideation”, Patent Application No. 15/379,013 filed on December 14, 2016 by Yale University Office of Cooperative Research
5. Arias A, Petrakis I, Krystal JH. – Composition and methods to treat addiction.
Provisional Use Patent Application no.61/973/961. April 2, 2014. Filed by Yale University Office of Cooperative Research.
6. Chekroud, A., Gueorguieva, R., & Krystal, JH. “Treatment Selection for Major Depressive Disorder” [filing date 3rd June 2016, USPTO docket number Y0087.70116US00]. Provisional patent submission by Yale University
7. Gihyun, Yoon, Petrakis I, Krystal JH – Compounds, Compositions and Methods for Treating or Preventing Depression and Other Diseases. U. S. Provisional Patent Application No. 62/444,552, filed on
January10, 2017 by Yale University Office of Cooperative Research OCR 7088 US01
8. Abdallah, C, Krystal, JH, Duman, R, Sanacora, G. Combination Therapy for Treating or Preventing Depression or Other Mood Diseases. U.S. Provisional Patent Application No. 62/719,935 filed on August 20, 2018 by Yale University Office of Cooperative Research OCR 7451 US01
9. John Krystal, Godfrey Pearlson, Stephanie O’Malley, Marc Potenza, Fabrizio Gasparini, Baltazar Gomez-Mancilla, Vincent Malaterre. Mavoglurant in treating gambling and gaming disorders. U.S. Provisional Patent Application No. 63/125,181filed on December 14, 2020 by Yale University Office of Cooperative Research OCR 8065 US00
NON Federal Research Support
AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals provides the drug, Saracatinib, for research related to NIAAA grant “Center for Translational Neuroscience of Alcoholism [CTNA-4]
Novartis provides the drug, Mavoglurant, for research related to NIAAA grant “Center for Translational Neuroscience of Alcoholism [CTNA-4]
Cerevel provides the drug PF-06412562 for A Translational and Neurocomputational Evaluation of a D1R Partial Agonist for Schizophrenia (1 U01 MH121766-01)
Figures

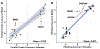
References
-
- Schmitt DP, Realo A, Voracek M, Allik J (2008): Why can’t a man be more like a woman? Sex differences in Big Five personality traits across 55 cultures. J Pers Soc Psychol. 94:168–182. - PubMed
-
- South SC, Jarnecke AM, Vize CE (2018): Sex differences in the Big Five model personality traits: A behavior genetics exploration. Journal of Research in Personality. 74:158–165.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

