Comparison of Incremental Shuttle Walking Test, 6-Minute Walking Test, and Cardiopulmonary Exercise Stress Test in Patients with Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 36245105
- PMCID: PMC9585920
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.938140
Comparison of Incremental Shuttle Walking Test, 6-Minute Walking Test, and Cardiopulmonary Exercise Stress Test in Patients with Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
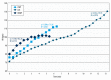
BACKGROUND This study aimed to analyze the correlations among peak oxygen uptake (VO2) in cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPX), incremental shuttle walking test (ISWT), and 6-minute walking test (6MWT) distances in patients with myocardial infarction (MI). Additionally, we aimed to determine the relationship between the maximum heart rate (HRmax) and the rate of perceived exertion (RPE) among the tests and compare the changes in heart rate to verify the clinical benefit of the submaximal stress test. MATERIAL AND METHODS We analyzed the correlation by using the ISWT and 6MWT at 30-min intervals after 24 h of CPX in patients with MI. The differences in HRmax and RPE between the tests were also compared. Additionally, changes in heart rate were analyzed using descriptive statistics. RESULTS The ISWT distance was more strongly correlated with peak VO₂ (r=.823: 95% CI, 0.681-0.910) than was 6MWT (r=0.776: 95% CI, 0.683-0.870). HRmax in the CPX demonstrated a significant correlation with that in the ISWT and 6MWT (P<0.05), with the ISWT (r=0.815: 95% CI, 0.451-0.996) having a stronger correlation than the 6MWT (r=0.664: 95% CI, 0.146-0.911). The value of RPE was significantly different (P<0.05); however, there was no significant correlation. Changes in heart rate in the 6MWT plateaued after the initial increase, while the heart rate in the ISWT and CPX increased gradually. CONCLUSIONS We recommend the ISWT as a submaximal exercise test to evaluate exercise capacity in patients with MI.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stronger correlation of peak oxygen uptake with distance of incremental shuttle walk test than 6-min walk test in patients with COPD: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Pulm Med. 2022 Mar 24;22(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-01897-0. BMC Pulm Med. 2022. PMID: 35331171 Free PMC article.
-
Which field walking test should be used to assess functional exercise capacity in lung cancer? An observational study.BMC Pulm Med. 2015 Aug 12;15:89. doi: 10.1186/s12890-015-0075-2. BMC Pulm Med. 2015. PMID: 26264470 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of exercise capacity using field walking tests in patients after the Fontan procedure: A case-control study.Heart Lung. 2023 Jul-Aug;60:66-73. doi: 10.1016/j.hrtlng.2023.02.022. Epub 2023 Mar 14. Heart Lung. 2023. PMID: 36924606
-
Are cardiovascular and metabolic responses to field walking tests interchangeable and obesity-dependent?Disabil Rehabil. 2016 Sep;38(18):1820-9. doi: 10.3109/09638288.2015.1107645. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Disabil Rehabil. 2016. PMID: 26681386
-
Submaximal Field Walking Tests Applied in the Cardiopulmonary Assessment in Congenital Heart Diseases: A Systematic Review.Curr Pediatr Rev. 2024;21(1):56-66. doi: 10.2174/0115733963263592231127042702. Curr Pediatr Rev. 2024. PMID: 38251699
Cited by
-
Heart rate reactivity, recovery, and endurance of the incremental shuttle walk test in patients prone to heart failure.ESC Heart Fail. 2024 Dec;11(6):4116-4126. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.15000. Epub 2024 Aug 11. ESC Heart Fail. 2024. PMID: 39129059 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Moxibustion for declined cardiorespiratory fitness of apparently healthy older adults: A study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 9;19(4):e0301673. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301673. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38593172 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Exercise Capacity in Post-COVID-19 Patients: How Is the Appropriate Test Chosen?Life (Basel). 2023 Feb 23;13(3):621. doi: 10.3390/life13030621. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36983777 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kasper D, Fauci A, Hauser S, et al. Harrison’s principles of internal medicine. 19th ed. Mcgraw-hill; 2015.
-
- Smith SC, Benjamin EJ, Bonow RO, et al. AHA/ACCF secondary prevention and risk reduction therapy for patients with coronary and other atherosclerotic vascular disease: 2011 update: A guideline from the American Heart Association and American College of Cardiology Foundation endorsed by the World Heart Federation and the Preventive Cardiovascular Nurses Association. Circulation. 2011;58(23):2432–46. - PubMed
-
- Group JJW. Guidelines for rehabilitation in patients with cardiovascular disease (JCS 2012) Circ J. 2014;78(8):2022–93. - PubMed
-
- Piepoli MF, Hoes AW, Agewall S, et al. 2016 European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice. Kardiol Pol. 2016;74(9):821–936. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical