Self-assisting robot-assisted pulmonary lobectomy has favorable outcome compared to VATS lobectomy
- PMID: 36245613
- PMCID: PMC9562502
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-22-176
Self-assisting robot-assisted pulmonary lobectomy has favorable outcome compared to VATS lobectomy
Abstract
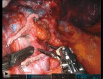
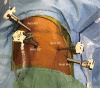
Background: Open and video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) pulmonary lobectomy requires a skilled assistant to complete the operation. A potential benefit of a robot is to allow a surgeon to complete the operation autonomously. We sought to determine the safety of performing robotic-assisted pulmonary lobectomy with self-assistance.
Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of self-assisting robot-assisted lobectomy. We evaluated the intraoperative and postoperative outcomes. We compared the outcome to the propensity matched group of patients who had VATS lobectomy. We also compared them to published outcomes of robot-assisted lobectomy.
Results: 95 patients underwent self-assisted lobectomies. The median age was 70 years old, predominately female (57%) and white (85%) with 90% of patients undergoing surgery for cancer. The median of estimated blood loss was 25 mL during the operation with no conversions to open thoracotomies. After the operation, 17% of patients had major postoperative complications with a median length of stay of 2 days. At thirty-day follow-up, the readmission rate was 6.5%, with a mortality of 0%. Compared to the propensity matched VATS lobectomy group, there was significantly less conversion to open surgery (n=0, 0% vs. n=10, 12.2%, P=0.002), less intraoperative blood transfusions (n=0, 0% vs. n=6, 7.3%, P=0.03), less any complications (n=20, 24.4% vs. n=41, 50%, P=0.003), and less median length of stay (2 days, IQR 2, 5 days vs. 4 day, IQR 3, 6 days, P<0.001) in the self-assisting robot lobectomy group. Compared to published outcomes of robot-assisted lobectomy, our series had significantly fewer conversions to open (P=0.03), shorter length of stay (P<0.001), more discharges to home (93.7%) without a difference in procedure time (P=0.38), overall complication rates (P=0.16) and mortality (P=0.62).
Conclusions: Self-assistance using the robot technology during pulmonary lobectomy had few technical complications and acceptable morbidity, length of stay, and mortality. This group had favorable outcome compared to VATS lobectomy. The ability to self-assist during pulmonary lobectomy is an additional benefit of the robot technology compared to open and VATS lobectomy.
Keywords: Robot lobectomy; autonomy; robot-assisted lobectomy; robotic lobectomy; self-assisting; video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery lobectomy (VATS lobectomy).
2022 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-22-176/coif). MPK consults for Veran/Olympus, Medtronic, AstraZeneca, and Intuitive Surgical. He serves as an unpaid editorial board member of Journal of Thoracic Disease from September 2020 to August 2022. EYC consults for Veran/Olympus and Intuitive Surgical. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hospital cost and clinical effectiveness of robotic-assisted versus video-assisted thoracoscopic and open lobectomy: A propensity score-weighted comparison.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2019 May;157(5):2018-2026.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2018.12.101. Epub 2019 Jan 23. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2019. PMID: 30819575
-
Open, Video- and Robot-Assisted Thoracoscopic Lobectomy for Stage II-IIIA Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Ann Thorac Surg. 2023 Jan;115(1):184-190. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2022.01.026. Epub 2022 Feb 8. Ann Thorac Surg. 2023. PMID: 35149049
-
Comparing robot-assisted thoracic surgical lobectomy with conventional video-assisted thoracic surgical lobectomy and wedge resection: results from a multihospital database (Premier).J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014 Mar;147(3):929-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2013.09.046. Epub 2013 Nov 8. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014. PMID: 24210834
-
Is the learning curve for video-assisted thoracoscopic lobectomy affected by prior experience in open lobectomy?Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2015 Jul;21(1):108-12. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivv090. Epub 2015 Apr 15. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2015. PMID: 25878186 Review.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of robotic versus open and video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery approaches for lobectomy.Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2019 Apr 1;28(4):526-534. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivy315. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2019. PMID: 30496420
Cited by
-
Robotic right lower lobectomy for a persistent large pulmonary arteriovenous malformation following repeated coil embolization.J Vasc Surg Cases Innov Tech. 2024 Aug 22;10(6):101605. doi: 10.1016/j.jvscit.2024.101605. eCollection 2024 Dec. J Vasc Surg Cases Innov Tech. 2024. PMID: 39314857 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
