Intraoperative fluorescence imaging in esophagectomy and its application to the robotic platform: a narrative review
- PMID: 36245633
- PMCID: PMC9562500
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-22-456
Intraoperative fluorescence imaging in esophagectomy and its application to the robotic platform: a narrative review
Abstract
Background and objective: Robotic-assisted esophagectomy is an approach to minimally invasive esophagectomy (MIE) that has demonstrated equivalent or improved outcomes relative to open and other minimally invasive techniques. The robotic approach also allows unique opportunities to improve complications following esophagectomy through use of enhanced visualization tools, including intraoperative fluorescence imaging. In this review, we summarize the specific uses of intraoperative fluorescence imaging as an adjunct tool during esophagectomy and discuss its application to the robotic platform.
Methods: A literature search was conducted via PubMed in February 2022 with the following keywords: esophagectomy, esophageal cancer, infrared, near-infrared (NIR) and fluorescence. Peer-reviewed academic journal articles published in English between 2000 and 2021 were included.
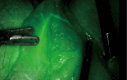
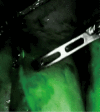
Key content and findings: There is a growing body of literature evaluating the use of intraoperative fluorescence imaging in robotic-assisted esophagectomy. This includes assessment of gastric conduit perfusion, including feasibility, creation of the gastroesophageal anastomosis, and qualification of perfusion, along with lymphatic mapping and identification of critical anatomy. These tools are uniquely leveraged using the robotic platform to standardize and quantify key technical aspects of the operation.
Conclusions: Intraoperative fluorescence imaging provides the opportunity to assess perfusion and identify anatomy for more precise and patient-specific dissection and reconstruction. Among all the operative techniques for esophagectomy, robotic-assisted esophagectomy is uniquely suited to utilize these imaging modalities to optimize outcomes and minimize risk associated with esophagectomy.
Keywords: Intraoperative fluorescence; esophagectomy; near-infrared imaging (NIR imaging); robotic-assisted.
2022 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-22-456/coif). LYS serves as an unpaid editorial board member of Journal of Thoracic Disease from April 2022 to March 2024. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intraoperative near-infrared fluorescence imaging as an adjunct to robotic-assisted minimally invasive esophagectomy.Innovations (Phila). 2014 Sep-Oct;9(5):391-3. doi: 10.1097/IMI.0000000000000091. Innovations (Phila). 2014. PMID: 25238427 Free PMC article.
-
Indocyanine green perfusion assessment of the gastric conduit in minimally invasive Ivor Lewis esophagectomy.Surg Endosc. 2022 Feb;36(2):896-903. doi: 10.1007/s00464-021-08346-9. Epub 2021 Feb 12. Surg Endosc. 2022. PMID: 33580319
-
Robotic-assisted Ivor Lewis esophagectomy, a review of the technique.Updates Surg. 2021 Jun;73(3):831-838. doi: 10.1007/s13304-021-01000-y. Epub 2021 May 20. Updates Surg. 2021. PMID: 34014498 Review.
-
Near-infrared fluorescence imaging of thoracic duct in minimally invasive esophagectomy.Dis Esophagus. 2023 Jan 28;36(2):doac049. doi: 10.1093/dote/doac049. Dis Esophagus. 2023. PMID: 35849094 Clinical Trial.
-
Robotic-assisted minimally invasive esophagectomy versus the conventional minimally invasive one: A meta-analysis and systematic review.Int J Med Robot. 2019 Jun;15(3):e1988. doi: 10.1002/rcs.1988. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Int J Med Robot. 2019. PMID: 30737881
Cited by
-
The use of indocyanine green (ICYG) angiography intraoperatively to evaluate gastric conduit perfusion during esophagectomy: does it impact surgical decision-making?Surg Endosc. 2023 Nov;37(11):8720-8727. doi: 10.1007/s00464-023-10258-9. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Surg Endosc. 2023. PMID: 37530987
References
-
- Abdelfatah E, Jordan S, Dexter EU, Nwogu C. Robotic thoracic and esophageal surgery: a critical review of comparative outcomes. Ann Laparosc Endosc Surg 2021;6:10. 10.21037/ales.2020.04.03 - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous