An Integrated Strategy of Chemical Fingerprint and Network Pharmacology for the Discovery of Efficacy-Related Q-Markers of Pheretima
- PMID: 36245784
- PMCID: PMC9553678
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8774913
An Integrated Strategy of Chemical Fingerprint and Network Pharmacology for the Discovery of Efficacy-Related Q-Markers of Pheretima
Abstract
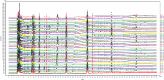
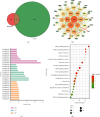
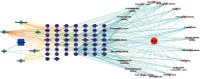
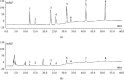
Pheretima, one of the animal-derived traditional Chinese medicines, has been wildly used in various cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, including stroke, coronary heart disease, hyperlipidemia, and hyperglycemia. However, it was still a big challenge to select the quality markers for Pheretima quality control. The fingerprint and network pharmacology-based strategy was proposed to screen the efficiency related quality markers (Q-Markers) of Pheretima. The ratio of sample to liquid, ultrasonic-extraction time, temperature, and power were optimized by orthogonal design, respectively. The chemical fingerprint of forty batches of Pheretima was established, and six common peaks were screened. The network pharmacology was used to construct the Pheretima-Components-Targets-Pathways-Stroke network. It was found that six potential efficacy Q-markers in Pheretima could exert the relaxing meridians effect to treat stroke through acting on multiple targets and regulating various pathways. A simple HPLC-DAD method was developed and validated to determine the efficacy Q-markers. Grey relational analysis was used to further verify the relation of potential efficiency related quality markers with the anticoagulation activity of Pheretima, which indicated that the contents of these markers exhibited high relationship with the anticoagulation activity. It was concluded that hypoxanthine, uridine, phenylalanine, inosine, guanosine, and tryptophan were selected as quality markers related to relaxing meridians to evaluate the quality of Pheretima. The fingerprint and network pharmacology-based strategy was proved to be a powerful strategy for the discovery of efficiency related Q-markers of Pheretima.
Copyright © 2022 Ye Shang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A multi-strategy platform for quality control and Q-markers screen of Chaiqin chengqi decoction.Phytomedicine. 2021 May;85:153525. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153525. Epub 2021 Feb 20. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33740732
-
A strategy integrated DNA barcoding with metabolomics for screening distinguishable combinatorial chemical quality marker between Pheretima aspergillum and Pheretima vulgaris Chen.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2025 May 15;257:116716. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2025.116716. Epub 2025 Jan 29. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2025. PMID: 39893778
-
Discovery of potential Q-marker of traditional Chinese medicine based on chemical profiling, chemometrics, network pharmacology, and molecular docking: Centipeda minima as an example.Phytochem Anal. 2022 Dec;33(8):1225-1234. doi: 10.1002/pca.3173. Epub 2022 Sep 18. Phytochem Anal. 2022. PMID: 36117130
-
[Prediction of Q-markers of Astragali Radix based on network pharmacology and fingerprint].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Jun;46(11):2691-2698. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200925.201. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34296565 Review. Chinese.
-
[Predictive analysis of quality markers of Coptidis Rhizoma based on network pharmacology and multivariate statistical analysis].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Jun;46(11):2718-2727. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210125.302. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34296568 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Identification of Key Mitochondrial Autophagy-Related Genes in Fetal Growth Restriction.Int J Womens Health. 2025 May 5;17:1249-1261. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S510947. eCollection 2025. Int J Womens Health. 2025. PMID: 40351334 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

