Differentially expressed genes related to lymph node metastasis in advanced laryngeal squamous cell cancers
- PMID: 36245825
- PMCID: PMC9555062
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2022.13529
Differentially expressed genes related to lymph node metastasis in advanced laryngeal squamous cell cancers
Abstract
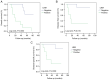
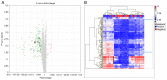
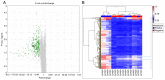
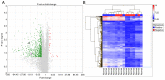
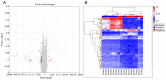
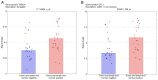
Understanding the molecular mechanisms and gene expression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) may explain its aggressive biological behavior and regional metastasis pathways. In the present study, patients with locally advanced LSCC tumors were examined for differential gene expression in the normal mucosa (non-tumoral mucosa), tumors and lymph node tissues. The aim was to identify possible predictive genes for lymph node metastasis. A total of 16 patients who had undergone total laryngectomy with neck dissection for advanced LSCC were randomly selected from a hospital database: Eight of the patients had lymph node metastasis (Group 1) and the other eight patients did not have metastasis (Group 2). Overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS) and disease-specific survival (DSS) were analyzed. For each patient, paraffin-embedded tissue samples were collected from non-tumoral mucosa, tumoral lesions and lymph node tissues. RNA was extracted from the tissue samples and used for complementary DNA synthesis, and microarray analysis was subsequently performed on each sample. Gene expression levels were determined in each specimen, and Groups 1 and 2 were compared and statistically analyzed. The microarray results for lymph node metastasis-positive and -negative groups, indicated the differential expression of 312 genes in the lymph nodes, 691 genes in the normal mucosal tissue and 93 genes in the tumor tissue. Transgelin (TAGLN) and cofilin 1 (CFL1) were identified as possible target genes and validated using reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). The RT-qPCR results for TAGLN and CFL1 supported the microarray data. OS, DFS and DSS times were longer in Group 2 than in Group 1 (P=0.002, 0.015 and 0.009, respectively). In addition, TAGLN and CFL1 were associated with DFS and DSS. On the basis of these results, it is suggested that TAGLN and CFL1 expression may play an important role in the pathogenesis of regional metastasis and poor prognosis in advanced LSCC.
Keywords: cofilin-1; gene expression profile; laryngeal squamous cell cancer; microarray; tansgelin.
Copyright: © Bayır et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microarray gene expression analysis of tumorigenesis and regional lymph node metastasis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 26;8(12):e84854. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084854. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24386425 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
HOX genes: potential candidates for the progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2016 Nov;37(11):15087-15096. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5356-8. Epub 2016 Sep 22. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27658780
-
[Expression of the metastasis-associated gene 1 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma: correlation with cervical lymph node metastasis].Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Za Zhi. 2003 Jun;38(3):213-6. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Za Zhi. 2003. PMID: 14515783 Chinese.
-
High BAX/BCL2 mRNA ratio predicts favorable prognosis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma, particularly in patients with negative lymph nodes at the time of diagnosis.Clin Biochem. 2016 Aug;49(12):890-6. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2016.04.010. Epub 2016 Apr 26. Clin Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27129795
-
High expression of NDRG3 associates with positive lymph node metastasis and unfavourable overall survival in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Pathology. 2016 Dec;48(7):691-696. doi: 10.1016/j.pathol.2016.08.005. Epub 2016 Oct 22. Pathology. 2016. PMID: 27780595
Cited by
-
Personalized Treatment Strategies via Integration of Gene Expression Biomarkers in Molecular Profiling of Laryngeal Cancer.J Pers Med. 2024 Oct 10;14(10):1048. doi: 10.3390/jpm14101048. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39452555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Berberine inhibits the malignant cell phenotype by inactivating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Histol Histopathol. 2024 Nov;39(11):1527-1536. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-753. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Histol Histopathol. 2024. PMID: 38712806
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO), corp-author WHO; Geneva: 2014. World Cancer Report 2014; pp. 422–435.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
