Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of newly detected synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists AB-4CN-BUTICA, MMB-4CN-BUTINACA, MDMB-4F-BUTICA, MDMB-4F-BUTINACA and their analogs
- PMID: 36245876
- PMCID: PMC9558907
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1010501
Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of newly detected synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists AB-4CN-BUTICA, MMB-4CN-BUTINACA, MDMB-4F-BUTICA, MDMB-4F-BUTINACA and their analogs
Abstract
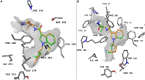
Synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists (SCRAs) continue to make up a significant portion new psychoactive substances (NPS) detected and seized worldwide. Due to their often potent activation of central cannabinoid receptors in vivo, use of SCRAs can result in severe intoxication, in addition to other adverse health effects. Recent detections of AB-4CN-BUTICA, MMB-4CN-BUTINACA, MDMB-4F-BUTICA and MDMB-4F-BUTINACA mark a continuation in the appearance of SCRAs bearing novel tail substituents. The proactive characterization campaign described here has facilitated the detection of several new SCRAs in toxicological case work. Here we detail the synthesis, characterization, and pharmacological evaluation of recently detected SCRAs, as well as a systematic library of 32 compounds bearing head, tail, and core group combinations likely to appear in future. In vitro radioligand binding assays revealed most compounds showed moderate to high affinity at both CB1 (pK i = < 5 to 8.89 ± 0.09 M) and CB2 (pK i = 5.49 ± 0.03 to 9.92 ± 0.09 M) receptors. In vitro functional evaluation using a fluorescence-based membrane potential assay showed that most compounds were sub-micromolar to sub-nanomolar agonists at CB1 (pEC50 = < 5 to 9.48 ± 0.14 M) and CB2 (pEC50 = 5.92 ± 0.16 to 8.64 ± 0.15 M) receptors. An in silico receptor-ligand docking approach was utilized to rationalize binding trends for CB2 with respect to the tail substituent, and indicated that rigidity in this region (i.e., 4-cyanobutyl) was detrimental to affinity.
Keywords: SCRAs; cannabinoid receptor 1 agonists; cannabinoids; docking; in vitro evaluation; pharmacology; synthesis; synthetic cannabinoid.
Copyright © 2022 Sparkes, Boyd, Chen, Markham, Luo, Foyzun, Zaman, Fletcher, Ellison, McGregor, Santiago, Lai, Gerona, Connor, Hibbs, Cairns, Glass, Ametovski and Banister.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
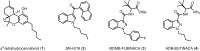
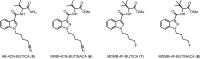

Similar articles
-
Systematic evaluation of a panel of 30 synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists structurally related to MMB-4en-PICA, MDMB-4en-PINACA, ADB-4en-PINACA, and MMB-4CN-BUTINACA using a combination of binding and different CB1 receptor activation assays: Part I-Synthesis, analytical characterization, and binding affinity for human CB1 receptors.Drug Test Anal. 2021 Jul;13(7):1383-1401. doi: 10.1002/dta.3037. Epub 2021 May 6. Drug Test Anal. 2021. PMID: 33787091
-
Systematic evaluation of a panel of 30 synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists structurally related to MMB-4en-PICA, MDMB-4en-PINACA, ADB-4en-PINACA, and MMB-4CN-BUTINACA using a combination of binding and different CB1 receptor activation assays-Part II: Structure activity relationship assessment via a β-arrestin recruitment assay.Drug Test Anal. 2021 Jul;13(7):1402-1411. doi: 10.1002/dta.3035. Epub 2021 Apr 14. Drug Test Anal. 2021. PMID: 33769699
-
In vitro CB1 receptor activity of halogenated indazole synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists.Arch Toxicol. 2025 Aug;99(8):3343-3353. doi: 10.1007/s00204-025-04082-4. Epub 2025 May 18. Arch Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40382747 Free PMC article.
-
The Chemistry and Pharmacology of Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists as New Psychoactive Substances: Origins.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2018;252:165-190. doi: 10.1007/164_2018_143. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29980914 Review.
-
Synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists: classification and nomenclature.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2020 Feb;58(2):82-98. doi: 10.1080/15563650.2019.1661425. Epub 2019 Sep 16. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2020. PMID: 31524007 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis and functional evaluation of proteinogenic amino acid-derived synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists related to MPP-5F-PICA, MMB-5F-PICA, and MDMB-5F-PICA.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Apr 10;15(6):2063-2079. doi: 10.1039/d3md00758h. eCollection 2024 Jun 19. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38911147 Free PMC article.
-
A sleepy cannabis constituent: cannabinol and its active metabolite influence sleep architecture in rats.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2025 Feb;50(3):586-595. doi: 10.1038/s41386-024-02018-7. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 39528623 Free PMC article.
-
Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) for the Binding Kinetics Analysis of Synthetic Cannabinoids: Advancing CB1 Receptor Interaction Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 14;26(8):3692. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083692. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332355 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro metabolism of Benzyl-4CN-BUTINACA and MDMB-4CN-BUTINACA using human hepatocytes and LC-QToF-MS analysis.Arch Toxicol. 2025 Jun;99(6):2355-2366. doi: 10.1007/s00204-025-04018-y. Epub 2025 Mar 18. Arch Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40097708 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UNODC . World Drug Report 2021 (2021).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

