Machine learning for autism spectrum disorder diagnosis using structural magnetic resonance imaging: Promising but challenging
- PMID: 36246393
- PMCID: PMC9554556
- DOI: 10.3389/fninf.2022.949926
Machine learning for autism spectrum disorder diagnosis using structural magnetic resonance imaging: Promising but challenging
Abstract
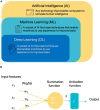
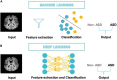
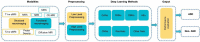
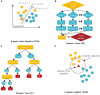
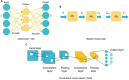
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder that affects approximately 1% of the population and causes significant burdens. ASD's pathogenesis remains elusive; hence, diagnosis is based on a constellation of behaviors. Structural magnetic resonance imaging (sMRI) studies have shown several abnormalities in volumetric and geometric features of the autistic brain. However, inconsistent findings prevented most contributions from being translated into clinical practice. Establishing reliable biomarkers for ASD using sMRI is crucial for the correct diagnosis and treatment. In recent years, machine learning (ML) and specifically deep learning (DL) have quickly extended to almost every sector, notably in disease diagnosis. Thus, this has led to a shift and improvement in ASD diagnostic methods, fulfilling most clinical diagnostic requirements. However, ASD discovery remains difficult. This review examines the ML-based ASD diagnosis literature over the past 5 years. A literature-based taxonomy of the research landscape has been mapped, and the major aspects of this topic have been covered. First, we provide an overview of ML's general classification pipeline and the features of sMRI. Next, representative studies are highlighted and discussed in detail with respect to methods, and biomarkers. Finally, we highlight many common challenges and make recommendations for future directions. In short, the limited sample size was the main obstacle; Thus, comprehensive data sets and rigorous methods are necessary to check the generalizability of the results. ML technologies are expected to advance significantly in the coming years, contributing to the diagnosis of ASD and helping clinicians soon.
Keywords: autism spectrum disorder (ASD); biomarkers; deep learning; machine learning; structural magnetic resonance imaging (sMRI).
Copyright © 2022 Bahathiq, Banjar, Bamaga and Jarraya.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
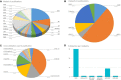
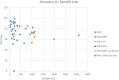
References
-
- Ahmad H. A., Yu H. J., Miller C. G. (2014). “Medical imaging modalities,” in Medical imaging in clinical trials (Berlin: Springer; ), 3–26. 10.1007/978-1-84882-710-3_1 - DOI
-
- Ali M. T., Elnakieb Y. A., Shalaby A., Mahmoud A., Switala A., Ghazal M., et al. (2021). “Autism classification using smri: A recursive features selection based on sampling from multi-level high dimensional spaces,” in Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 18th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE; ), 267–270. 10.1109/ISBI48211.2021.9433973 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

