Study on complications of osteoporosis based on network pharmacology
- PMID: 36246605
- PMCID: PMC9557205
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.941098
Study on complications of osteoporosis based on network pharmacology
Abstract
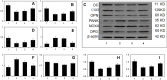
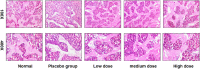
Osteoporosis is a serious threat to human life. Guben Zenggu Granule is an empirical prescription for clinical treatment of osteoporosis. MC3T3-E1 cells are mouse osteogenic precursor cells with osteogenic differentiation, and are classic cells for studying bone metabolism and osteogenic mechanism, as well as mechanical stimulation sensitive cells. Therefore, it can be inferred that Guben Zenggu granule can repair MC3T3-E1 cells under continuous static pressure overload. This study aims to through the network of pharmacology and gene sequencing method, reveal thrift increase bone particles under the condition of continuous static pressure overload on osteogenesis mechanism of MC3T3-E1 cells. In the process of analysis, from a variety of 98 compounds was predicted in the database, a collection of 474 goals, a total of 29,164 difference between two groups of genes. Then, construction of composite targets between cells and predict targets and protein - protein interaction networks, and through the cluster analysis to further explore the relationship between the target. In addition, linkages between target proteins and cells were further identified using Gene Ontology (GO) and Pathways (KEGG Pathway). Finally, the repair effect of Guben Zenggu granule on MC3T3-E1 cells under continuous static pressure overload was verified through experiments, so as to accurately explain the pharmacodynamic mechanism of Traditional Chinese medicine.
Keywords: MC3T3-E1 cells; continuous static pressure; gene sequencing; guben zenggu granules; network pharmacology.
Copyright © 2022 Song, Zhang, Jiang, Zhao, Pei, Ning, Chen, Pan, Gong, Song and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
[Effect of Guben Zenggu Decoction on Expressions of Serum BALP and CaM, CaMKⅡ mRNA in NEI Network of Ovariectomized Rats].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019 Jan;50(1):27-33. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019. PMID: 31037901 Chinese.
-
Network Pharmacological Analysis and Animal Experimental Study on Osteoporosis Treatment with GuBen-ZengGu Granules.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Jan 12;2023:9317557. doi: 10.1155/2023/9317557. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 36686973 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of Guben Zenggu Decoction on Bone Metabolism and Bone Microstructure in Ovariectomized Rats].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019 Sep;50(5):679-683. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019. PMID: 31762237 Chinese.
-
Qiang Jin Mixture Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of MC3T3-E1 Cells via BMP2/Smads Pathway and its Network Pharmacology Study.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Nov 11. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01313-4. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39527391
-
The effects and mechanism of paeoniflorin in promoting osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1.J Orthop Surg Res. 2022 Feb 14;17(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-02965-1. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 35164817 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dong W., et al. (2018). Effects of Guben Zenggu Recipe on serum osteocalcin and free [Ca∼(2+)]i in NEI network tissue in ovariectomized rats[J]. Pharmacol. Chin. Med. Clin. 34 (01), 121
-
- Dong W., Gong Y. L., Song M., Huang K., Dong P., Song Z. J., et al. (2019). Effects of guben zenggu decoction on bone metabolism and bone microstructure in ovariectomized rats. J. Sichuan Univ. Med. Ed. 50 (05), 679–683. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

