Amivantamab in the Treatment of Metastatic NSCLC: Patient Selection and Special Considerations
- PMID: 36246734
- PMCID: PMC9555392
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S329095
Amivantamab in the Treatment of Metastatic NSCLC: Patient Selection and Special Considerations
Abstract
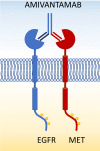
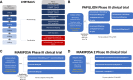
Amivantamab is a bispecific antibody that recognizes epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and MET proto-oncogene (MET). In May 2021, the Food and Drug Administration gave an accelerated approval of amivantamab for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with EGFR exon 20 insertions (Exon20ins) who progressed after platinum-based chemotherapy. Amivantamab prevents ligand binding to EGFR and MET and the dimerization of the receptors suppressing the downstream signal transduction. Moreover, amivantamab determines antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity and down regulation of cell surface proteins through internalization of the receptor and trogocytosis. Preliminary results of the Phase I/IB CHRYSALIS trial demonstrated an objective response rate of 40% with a median duration of response of 11.1 months (95% CI 9.6-not reached) in 81 patients treated with amivantamab with pretreated NSCLC with Exon20ins EGFR mutations. In a different cohort of the CHRYSALIS trial, patients with Ex19del and L858R EGFR mutations were enrolled after progression on osimertinib. 121 and 45 patients received amivantamab or a combination with lazertinib, a third-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor, respectively. The objective response rate was 19% and 36% in patients treated with amivantamab alone or in combination with lazertinib, with a median progression-free survival of 6.9 (95% CI: 3.2-5.3) and 11.1 (95% CI: 3.7-9.5) months, respectively. All 20 patients with Ex19del and L858R EGFR mutations who received amivantamab and lazertinib as their first line treatment achieved an objective response. Amivantamab is currently under evaluation in Phase III clinical trials for the first line treatment of NSCLCs with Exon20ins EGFR mutations in combination with chemotherapy (PAPILLON), for the first line therapy of Ex19del and L858R mutated NSCLCs in combination with lazertinib (MARIPOSA) and in combination with chemotherapy and lazertinib in NSCLCs who progressed on osimertinib (MARIPOSA-2).
Keywords: NSCLC; amivantamab; exon 20 insertion of EGFR.
© 2022 Petrini and Giaccone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

