Osteocytes and the pathogenesis of hypophosphatemic rickets
- PMID: 36246908
- PMCID: PMC9556901
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1005189
Osteocytes and the pathogenesis of hypophosphatemic rickets
Abstract
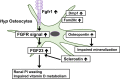
Since phosphorus is a component of hydroxyapatite, its prolonged deprivation affects bone mineralization. Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) is essential for maintaining phosphate homeostasis and is mainly produced by osteocytes. FGF23 increases the excretion of inorganic phosphate (Pi) and decreases the production of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D in the kidneys. Osteocytes are cells of osteoblastic lineage that have undergone terminal differentiation and become embedded in mineralized bone matrix. Osteocytes express FGF23 and other multiple genes responsible for hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets, which include phosphate-regulating gene homologous to endopeptidase on X chromosome (PHEX), dentin matrix protein 1 (DMP1), and family with sequence similarity 20, member C (FAM20C). Since inactivating mutations in PHEX, DMP1, and FAM20C boost the production of FGF23, these molecules might be considered as local negative regulators of FGF23. Mouse studies have suggested that enhanced FGF receptor (FGFR) signaling is involved in the overproduction of FGF23 in PHEX-deficient X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets (XLH) and DMP1-deficient autosomal recessive hypophosphatemic rickets type 1. Since FGFR is involved in the transduction of signals evoked by extracellular Pi, Pi sensing in osteocytes may be abnormal in these diseases. Serum levels of sclerostin, an inhibitor Wnt/β-catenin signaling secreted by osteocytes, are increased in XLH patients, and mouse studies have suggested the potential of inhibiting sclerostin as a new therapeutic option for the disease. The elucidation of complex abnormalities in the osteocytes of FGF23-related hypophosphatemic diseases will provide a more detailed understanding of their pathogenesis and more effective treatments.
Keywords: fibroblast growth factor 23; mutation; osteocyte; phosphate; rickets.
Copyright © 2022 Yamazaki and Michigami.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

