Recent updates on anticancer mechanisms of polyphenols
- PMID: 36247004
- PMCID: PMC9557130
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1005910
Recent updates on anticancer mechanisms of polyphenols
Abstract
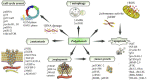
In today's scenario, when cancer cases are increasing rapidly, anticancer herbal compounds become imperative. Studies on the molecular mechanisms of action of polyphenols published in specialized databases such as Web of Science, Pubmed/Medline, Google Scholar, and Science Direct were used as sources of information for this review. Natural polyphenols provide established efficacy against chemically induced tumor growth with fewer side effects. They can sensitize cells to various therapies and increase the effectiveness of biotherapy. Further pharmacological translational research and clinical trials are needed to evaluate theirs in vivo efficacy, possible side effects and toxicity. Polyphenols can be used to design a potential treatment in conjunction with existing cancer drug regimens such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Keywords: anticancer molecular mechanisms; cancer; invasion; migration; pharmacology; phytochemicals; polyphenols.
Copyright © 2022 Sharma, Attri, Sati, Dhyani, Szopa, Sharifi-Rad, Hano, Calina and Cho.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Almatroodi S. A., Almatroudi A., Khan A. A., Alhumaydhi F. A., Alsahli M. A., Rahmani A. H. (2020). Potential therapeutic targets of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), the most abundant catechin in green tea, and its role in the therapy of various types of cancer. Molecules 25, E3146. 10.3390/molecules25143146 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

