Standardized quality control management improves rehabilitation of children with cerebral palsy in Ningbo City
- PMID: 36247265
- PMCID: PMC9556487
Standardized quality control management improves rehabilitation of children with cerebral palsy in Ningbo City
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effect of standardized quality control management on the rehabilitation of children with palsy in Ningbo City.
Methods: In this retrospective study, a total of 400 pediatric patients requiring rehabilitation therapy admitted to Ningbo Rehabilitation Hospital from July 2017 to May 2021, were selected as the research subjects. Pediatric patients were divided into an observation group (standardized model) and a control group (routine model) based on the different quality management models. The rehabilitation efficacy, nursing quality, negative emotion, satisfaction, DQ scores, ADL scores, PDI scores, MDI scores, compliance rate, complaint rate of nursing, and incidence of adverse events were compared between the two groups.
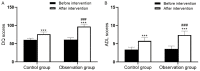
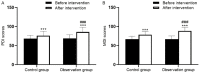
Results: The rehabilitation efficacy in the observation group was better than that in the control group (P<0.05). Compared to the control group, the nursing quality score and satisfaction rate were higher, and the negative emotion score was lower in the observation group (all P<0.05). DQ scores, ADL scores, PDI scores, and MDI scores in the observation group were higher than the control group (all P<0.05). The statistical differences were observed in the compliance rate, complaint rate in nursing, and incidence of adverse events between the two groups (all P<0.05).
Conclusions: The standardized quality control management enhanced the rehabilitation efficacy, promoted the nursing quality, improved the clinical effects, increased the satisfaction rate, and decreased the negative emotions in pediatric patients.
Keywords: Quality control management; clinical effects; nursing quality; pediatric rehabilitation; standardized model.
AJTR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Downs J, Blackmore AM, Epstein A, Skoss R, Langdon K, Jacoby P, Whitehouse AJO, Leonard H, Rowe PW, Glasson EJ Cerebral Palsy Mental Health Group. The prevalence of mental health disorders and symptoms in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2018;60:30–38. - PubMed
-
- Hollung SJ, Vik T, Wiik R, Bakken IJ, Andersen GL. Completeness and correctness of cerebral palsy diagnoses in two health registers: implications for estimating prevalence. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2017;59:402–406. - PubMed
-
- Birnkrant DJ, Bushby K, Bann CM, Apkon SD, Blackwell A, Brumbaugh D, Case LE, Clemens PR, Hadjiyannakis S, Pandya S, Street N, Tomezsko J, Wagner KR, Ward LM, Weber DR DMD Care Considerations Working Group. Diagnosis and management of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, part 1: diagnosis, and neuromuscular, rehabilitation, endocrine, and gastrointestinal and nutritional management. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17:251–267. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
