Molecular interaction between small nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptide G and heat shock protein 70.14: a microscale thermophoresis exposition towards developing anti-cancer drugs
- PMID: 36247303
- PMCID: PMC9556510
Molecular interaction between small nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptide G and heat shock protein 70.14: a microscale thermophoresis exposition towards developing anti-cancer drugs
Abstract
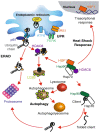
Background: Targeting protein-protein interactions (PPIs) linked to protein quality control (PQC) pathways as potential anti-cancer drug targets have unanimously widened biological insights and the therapeutic potential of PPIs as smart-drug discovery tools in cancer. PPIs between disease-relevant proteins associated with protein homeostasis in PQC pathways have been linked to improved mechanistic understanding associated with conformational abnormalities and impairment, cellular proteotoxicity, induced apoptosis, and pathogenesis in different types of cancers. In this context, PPIs between small nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptide G (SNRPG) and heat shock protein 70.14 (Hsp70.14) have attracted attention as potential smart drug discovery tools in cancer diagnostics and therapeutics. Validated evidence of high-quality biological data has shown the presence of the two proteins in different types of cancers including breast cancer. The links between SNRPG and Hsp70.14 in cancer-cell networks remain elusive, overlooked, and uncharacterized.
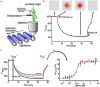
Methodology: In this study, we explored the interaction between the two oncogenic proteins using the MST-based assays.
Results: The results revealed a low KD in the nanomolar concentration range of 2.4673 × 10-7 demonstrating a great affinity for SNRPG binding to Hsp70.14.
Conclusions: The results suggest a possible involvement between the two proteins in hostile tumour microenvironments. Furthermore, these findings offer a different therapeutic perspective that could pave the way for the creation of novel small molecule inhibitors as drugs for the treatment of cancer.
Keywords: Anti-cancer drug discovery; Hsp70.14; SNRPG; dissociation constant; microscale thermophoresis; protein-protein interactions; proteostasis.
AJTR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Microscale thermophoresis analysis of the molecular interaction between small nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptide G and the RING finger domain of RBBP6 towards anti-cancer drug discovery.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Nov 15;13(11):12775-12785. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34956492 Free PMC article.
-
The oncogenic potential of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptide G: a comprehensive and perspective view.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Nov 15;11(11):6702-6716. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31814883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitors and chemical probes for molecular chaperone networks.J Biol Chem. 2019 Feb 8;294(6):2151-2161. doi: 10.1074/jbc.TM118.002813. Epub 2018 Sep 13. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30213856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATP1A3 Acts as a Potential Anti-oncogene in Glioblastoma via the Antagonizing Interaction with Small Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein Polypeptide G.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2025 Mar 11. doi: 10.2174/011570159X361656250128073206. Online ahead of print. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40070326
-
High-throughput screen for inhibitors of protein-protein interactions in a reconstituted heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) complex.J Biol Chem. 2018 Mar 16;293(11):4014-4025. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001575. Epub 2018 Feb 2. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29414793 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Díaz-Eufracio BI, Jesús Naveja J, Medina-Franco JL. Protein-protein interaction modulators for epigenetic therapies. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2018;110:65–84. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
