Prevalence and Risk Factors of Superficial Fungal Infection among Patients Attending a Tertiary Care Hospital in Central Nepal
- PMID: 36247346
- PMCID: PMC9553492
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3088681
Prevalence and Risk Factors of Superficial Fungal Infection among Patients Attending a Tertiary Care Hospital in Central Nepal
Abstract
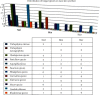
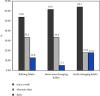
Fungal infections of hair, nail, and skin are common worldwide and tend to increase. The present study was conducted to determine the prevalence of dermatomycoses, estimate the efficiency of rapid potassium hydroxide (KOH) wet-mount, and observe the hygienic status and the predisposing risk factors. Altogether 115 samples (nail = 77, skin = 30, and hair = 8) were obtained in a duration of December 2019 to June 2020 at Grande International Hospital, Nepal. The samples were examined by KOH wet-mount microscopy and further processed for culture. The dermatophyte test medium (DTM) was used to isolate dermatophytes separately. The fungal colonies obtained in SDA, SDA with cycloheximide/chloramphenicol and dermatophyte medium were subjected to lactophenol cotton blue (LPCB) reagent to study fungal morphology. The yeast colonies grown on SDA were subjected to Gram staining, germ-tube tests, and biochemical tests for identification. CHROMagar was used to distinguish different Candida species based on its pigment production in the medium. Various factors (age, sex, occupation, and hygiene condition) were analyzed which were associated with mycological infection. Out of 115 samples, the presence of fungal elements was detected in 20 samples by KOH. Nondermatophyte molds were the most isolated fungus in nails, skin, and hair, followed by yeast and dermatophytes, respectively. Dermatomycosis molds were the most common causative agents with 22 (14.7%) cases, followed by yeasts with 6 (5.21%) cases. Candida albicans was isolated from 5 (4.3%) cases, whereas Rhodotorula species accounted for a single (0.8%) case. Dermatophytes were isolated from 5 (4.3%) cases. Among them, n = 4(3.4%) cases revealed Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes was isolated from single (0.8%) case. The most isolated nondermatophyte mold that follows criteria as a pathogen in our study was Cladosporium species 6 (25%) out of 27 total fungal isolates. Poor hygiene and sweating were found to be statistically significant (P < 0.05) in fungal cases detected by both KOH and culture. Dermatophytes and nondermatophyte fungi were emerging as important causes of fungal infection. Both direct microscopy and culture followed by LPCB together were vital tools for the diagnosis of fungal infections.
Copyright © 2022 Vidya Laxmi Jaishi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
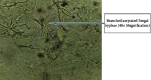

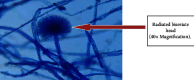
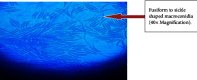
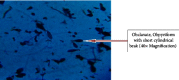
Similar articles
-
Epidemiological characterization of dermatophytes at a tertiary care hospital in Eastern Uttar Pradesh, India.Curr Med Mycol. 2019 Mar;5(1):1-6. doi: 10.18502/cmm.5.1.530. Curr Med Mycol. 2019. PMID: 31049451 Free PMC article.
-
Mycological Pattern of Dermatomycoses in a Tertiary Care Hospital.J Trop Med. 2015;2015:157828. doi: 10.1155/2015/157828. Epub 2015 Sep 30. J Trop Med. 2015. PMID: 26491453 Free PMC article.
-
Current Trends of Dermatophytosis in Eastern Odisha.J Lab Physicians. 2020 Mar;12(1):10-14. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1713063. Epub 2020 Jun 11. J Lab Physicians. 2020. PMID: 32792788 Free PMC article.
-
[Etiopathogenesis, clinical picture and diagnosis of onychomycoses].Med Pregl. 2001 Jan-Feb;54(1-2):45-51. Med Pregl. 2001. PMID: 11432322 Review. Croatian.
-
[Update on the diagnosis of dermatomycosis].Parassitologia. 2004 Jun;46(1-2):183-6. Parassitologia. 2004. PMID: 15305713 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
Nanosponge hydrogel of octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl) propanoate of Alcaligenes faecalis.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Dec;108(1):100. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12819-3. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38217256 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and preclinical evaluation of the antifungal activity of 6-methoxy-1 H-indole-2-carboxylic acid produced by Bacillus toyonensis strain OQ071612 formulated as nanosponge hydrogel.Microb Cell Fact. 2025 Apr 1;24(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s12934-025-02688-y. Microb Cell Fact. 2025. PMID: 40169999 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge and Practices of the Jeddah Population Towards Tinea Pedis: A Cross-Sectional Study.Cureus. 2025 Jun 20;17(6):e86460. doi: 10.7759/cureus.86460. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40693056 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Evans E., Gentles J. Essentials of Medical Mycology . Edinburgh, Scotland: Churchill Livingstone; 1985.
-
- Ogutu M., Ngang Z., Namasaka M., Wambura M. Superficial mycoses among psychiatric patients in mathari hospital, nairobi, Kenya. East African Medical Journal . 2010;87(9):360–367. - PubMed
-
- Hay R. J. Oxford Textbook Of Medicine: Warrell DA . Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press Section; 2003. Fungal infections (mycoses)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

