QTL mapping and KASP marker development for seed vigor related traits in common wheat
- PMID: 36247615
- PMCID: PMC9563228
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.994973
QTL mapping and KASP marker development for seed vigor related traits in common wheat
Abstract
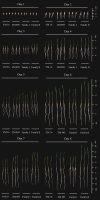
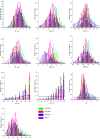
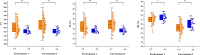
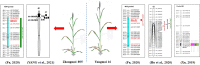
Seed vigor is an important parameter of seed quality, and identification of seed vigor related genes can provide an important basis for highly efficient molecular breeding in wheat. In the present study, a doubled haploid (DH) population with 174 lines derived from a cross between Yangmai16 and Zhongmai 895 was used to evaluate 10 seed vigor related traits in Luoyang during the 2018-2019 cropping season and in Mengjin and Luoning Counties during 2019-2020 cropping season for three environments. Quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping of 10 seed vigor related traits in the DH population resulted in the discovery/identification of 28 QTLs on chromosomes 2B, 3D, 4B, 4D, 5A, 5B, 6A, 6B, 6D, 7A and 7D, explaining 3.6-23.7% of the phenotypic variances. Among them, one QTL cluster for shoot length, root length and vigor index was mapped between AX-89421921 and Rht-D1_SNP on chromosome 4D in the physical intervals of 18.78-19.29 Mb (0.51 Mb), explaining 9.2-20.5% of the phenotypic variances. Another QTL for these traits was identified at the physical position 185.74 Mb on chromosome 5B, which was flanked by AX-111465230 and AX-109519938 and accounted for 8.0-13.3% of the phenotypic variances. Two QTLs for shoot length, shoot fresh weight and shoot dry weight were identified in the marker intervals of AX-109384026-AX-111120402 and AX-111651800-AX-94443918 on chromosomes 6A and 6B, explaining 8.2-11.7% and 3.6-10.3% of the phenotypic variance, respectively; both alleles for increasing phenotypic values were derived from Yangmai 16. We also developed the KASP markers for the QTL cluster QVI.haust-4D.1/QSL.haust-4D/QRL.haust-4D, and validated in an international panel of 135 wheat accessions. The germplasm, genes and KASP markers were developed for breeders to improve wheat varieties with seed vigor related traits.
Keywords: KASP marker; QTL cluster; QTLs; Triticum aestivum; seed vigor.
Copyright © 2022 Zeng, Guo, Yan, Song, Wang, Xu and Hao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification and validation of new quantitative trait loci for spike-related traits in two RIL populations.Mol Breed. 2023 Jul 31;43(8):64. doi: 10.1007/s11032-023-01401-4. eCollection 2023 Aug. Mol Breed. 2023. PMID: 37533603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
QTL mapping and candidate gene analysis of seed vigor-related traits during artificial aging in wheat (Triticum aestivum).Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 16;10(1):22060. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-75778-z. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33328518 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Validation of a Novel Locus Controlling Spikelet Number in Bread Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Front Plant Sci. 2021 Feb 26;12:611106. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.611106. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33719283 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Linkage Mapping Reveals QTLs for Seed Vigor-Related Traits Under Artificial Aging in Common Wheat (Triticum aestivum).Front Plant Sci. 2018 Jul 27;9:1101. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01101. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30100918 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution detection of quantitative trait loci for seven important yield-related traits in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) using a high-density SLAF-seq genetic map.BMC Genom Data. 2022 May 13;23(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12863-022-01050-0. BMC Genom Data. 2022. PMID: 35562674 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genetic Variation Analysis and Development of KASP Marker for Leaf Area and Hight in Southern-Type Populus deltoides.Plants (Basel). 2025 Jan 23;14(3):330. doi: 10.3390/plants14030330. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39942892 Free PMC article.
-
Development of KASP markers, SNP fingerprinting and population genetic analysis of Cymbidium ensifolium (L.) Sw. germplasm resources in China.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jan 8;15:1460603. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1460603. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 39845486 Free PMC article.
-
Genotype adaptive patterns in spring wheat reveal drought-induced differentiation in root morphology.Front Plant Sci. 2025 May 21;16:1534211. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1534211. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40470363 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of TaCRY Gene Family and Its Expression in Seed Aging Process of Wheat.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Jul 6;47(7):522. doi: 10.3390/cimb47070522. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40728991 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of new quantitative trait loci for spike-related traits in two RIL populations.Mol Breed. 2023 Jul 31;43(8):64. doi: 10.1007/s11032-023-01401-4. eCollection 2023 Aug. Mol Breed. 2023. PMID: 37533603 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Addisu M., Snape J. W., Simmonds J. R., Gooding M. J. (2008). Reduced height (Rht) and photoperiod insensitivity (Ppd) allele associations with establishment and early growth of wheat in contrasting production systems. Euphytica 166, 249–267. doi: 10.1111/ppl.13321 - DOI
-
- Botwright T., Rebetzke G., Condon T., Richards R. (2001). The effect of rht genotype and temperature on coleoptile growth and dry matter partitioning in young wheat seedlings. Funct. Plant Biol. 28, 417. doi: 10.1071/pp01010 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

