Tolerance for ambiguity, reappraisal, and suppression mediate the relationship between problematic internet use and procrastination
- PMID: 36248214
- PMCID: PMC9550598
- DOI: 10.1007/s12144-022-03745-0
Tolerance for ambiguity, reappraisal, and suppression mediate the relationship between problematic internet use and procrastination
Abstract
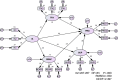
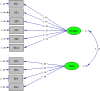
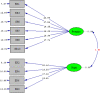
The current scientific literature lacks studies on the relationship between problematic internet use (PIU) and procrastination, especially regarding the mediating mechanisms underlying this relationship. The present study examined the association between procrastination and PIU, as well as determining the mediating roles of tolerance for ambiguity, reappraisal, and suppression. The conceptual model was tested using data collected from 434 Iranian college students. The participants completed a number of psychometric scales assessing procrastination, PIU, tolerance for ambiguity, reappraisal, and suppression. Structural equation modeling was used to test the hypothesized model. Results showed that PIU, tolerance for ambiguity, and suppression were positively associated with procrastination, and that there was a negative association between reappraisal and procrastination. Moreover, the mediation analysis indicated that tolerance for ambiguity, reappraisal, and suppression fully mediated the association between PIU and procrastination. However, it is also possible to interpret the results as suggesting that PIU is unimportant as a predictor for procrastination once mediators are controlled for.
Keywords: Problematic internet use; Procrastination; Reappraisal; Suppression; Tolerance for ambiguity.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestNone.
Figures



References
-
- Abolqasemi A, & Narimani M. (2005). Psychological tests [in Persian]. Ardebil:Razvand Bagh Publishing, 13(7), 10–17. [Persian].
-
- Alavi SS, Jannatifard F, Eslami M, Rezapour H. Survey on validity and reliability of diagnostic questionnaire of internet addiction disorder in students users. Zahedan Journal of Research in Medical Sciences. 2011;13(7):34–37.
-
- Amendola S, Spensieri V, Guidetti V, Cerutti R. The relationship between difficulties in emotion regulation and dysfunctional technology use among adolescents. Journal of Psychopathology. 2019;25(1):10–17.
-
- Anderson JC, Gerbing DW. Structural equation modeling in practice: A review and recommended two-step approach. Psychological Bulletin. 1988;103(3):411. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.103.3.411. - DOI
-
- Balzarotti S, John OP, Gross JJ. An Italian adaptation of the emotion regulation questionnaire. European Journal of Psychological Assessment. 2010;26(1):61–67. doi: 10.1027/1015-5759/a000009. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
