Zuo Jin Wan Reverses the Resistance of Colorectal Cancer to Oxaliplatin by Regulating the MALAT1/miR-200s/JNK Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 36248422
- PMCID: PMC9568309
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3032407
Zuo Jin Wan Reverses the Resistance of Colorectal Cancer to Oxaliplatin by Regulating the MALAT1/miR-200s/JNK Signaling Pathway
Abstract
Background: Oxaliplatin (L-OHP) is a common chemotherapy drug used in the treatment of colorectal cancer (CRC). Our previous work showed that Zuo Jin Wan (ZJW), a traditional Chinese medicine prescription, could improve sensitivity to L-OHP in the treatment of CRC, but the detailed mechanism is not clear. In previous mechanistic studies, we found that the miR-200s expression in CRC is associated with L-OHP sensitivity through regulation of MDR1/p-gp and the downstream c-JunN-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling pathway. Moreover, lncRNA-MALAT1 offers great potential in the regulation of drug resistance by interacting with miR-200s. Therefore, in this work, we explored whether ZJW could reverse L-OHP resistance in CRC by regulating MALAT1, miR-200s, and the downstream signaling pathway.
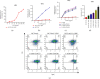
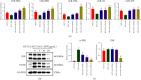
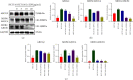
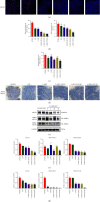
Methods: Cell Counting Kit-8 and flow cytometry were used to detect the effects of ZJW combined with L-OHP on chemotherapy tolerance and cell apoptosis of HCT116/L-OHP cells. Western blotting and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) were used to detect the activation of the JNK signaling pathway and the protein and mRNA expression levels of the drug resistance-related MDR1/ABCB1 gene in HCT116/L-OHP cells treated with ZJW. The binding sites of MALAT1 and miR-200s were predicted by bioinformatics tools and confirmed by qRT-PCR. qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression of miR-200s and MALAT1 in HCT116/L-OHP cells treated with ZJW. A xenograft model of CRC in nude mice was established to observe the effect of ZJW combined with L-OHP on the growth of subcutaneously transplanted tumors. Apoptosis in tumor cells was detected by TUNEL staining. The activation of the JNK signaling pathway and the expression of drug resistance-related proteins were detected by immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence. qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression of miR-200s and the MALAT1 gene in the tumors.
Results: Our study showed that ZJW could significantly decrease the proliferation and promote apoptosis of HCT116/L-OHP cells treated with L-OHP. We further proved that ZJW could reverse the drug resistance of HCT116/L-OHP cells by reducing MALAT1, indirectly upregulating miR-200s, alleviating the activation of the JNK signaling axis, and downregulating the expression of resistance proteins such as MDR1/ABCB1 and ABCG2. ZJW combined with L-OHP inhibited the growth of subcutaneously transplanted tumors and induced apoptosis in nude mice. ZJW reduced the expression of MALAT1 and upregulated the expression of miR-200s in transplanted tumors. In addition, ZJW also alleviated the activation of the JNK signaling pathway while reducing the expression of MDR1/ABCB1 and ABCG2.
Conclusions: Our study identified that MALAT1 promotes colorectal cancer resistance to oxaliplatin by reducing the miR-200s expression. ZJW may reverse chemoresistance by inhibiting the expression of MALAT1 and regulating the miR-200s/JNK pathway, providing an experimental basis for the clinical application of ZJW in relieving chemotherapy resistance.
Copyright © 2022 Zhenzhen Wei et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Zuo Jin Wan reverses P-gp-mediated drug-resistance by inhibiting activation of the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Aug 1;14:279. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-279. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 25085593 Free PMC article.
-
Zuo Jin Wan, a Traditional Chinese Herbal Formula, Reverses P-gp-Mediated MDR In Vitro and In Vivo.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:957078. doi: 10.1155/2013/957078. Epub 2013 Mar 4. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23533531 Free PMC article.
-
miR-506 enhances the sensitivity of human colorectal cancer cells to oxaliplatin by suppressing MDR1/P-gp expression.Cell Prolif. 2017 Jun;50(3):e12341. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12341. Epub 2017 Feb 19. Cell Prolif. 2017. PMID: 28217977 Free PMC article.
-
The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in colorectal cancer: mechanism and intervention of traditional Chinese medicine and chemical compound.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 10;16:1560714. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1560714. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40308773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress of traditional Chinese medicine as sensitizer in reversing chemoresistance of colorectal cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 13;13:1132141. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1132141. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36994201 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Zuo Jin Wan in Modulating the Tumor Microenvironment of Colorectal Cancer.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025;28(3):523-532. doi: 10.2174/0113862073281374231228041841. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025. PMID: 38284730
-
Upregulated lncRNA PRNT promotes progression and oxaliplatin resistance of colorectal cancer cells by regulating HIPK2 transcription.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Apr 15;16(4):1564-1577. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1564. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38660648 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of key lncRNAs associated with oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer cells and isolated exosomes: From In-Silico prediction to In-Vitro validation.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 14;19(10):e0311680. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311680. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39401197 Free PMC article.
-
The functions and mechanisms of long non-coding RNA in colorectal cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 4;14:1419972. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1419972. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39026978 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Petrelli F., Labianca R., Zaniboni A., et al. Assessment of duration and effects of 3 vs. 6 Months of adjuvant chemotherapy in high-risk stage II colorectal cancer: a subgroup Analysis of the tosca randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncology . 2020;6(4):547–551. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6486. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

