The role of empathy between peers in upper secondary students' study engagement and burnout
- PMID: 36248570
- PMCID: PMC9561899
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.978546
The role of empathy between peers in upper secondary students' study engagement and burnout
Abstract
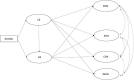
Having the ability to understand emotionally how other people feel and see things is an essential fabric for building and sustaining functional interpersonal relationships. Without such an ability, social interaction crumbles, engagement fails, and learning is eroded. Yet, empirical evidence on the relationship between study burnout and study engagement, and empathy between upper secondary school students is limited. We are tackling the challenge by exploring the association between empathy between peers and study engagement and study burnout among upper secondary school students. Two hundred and eighty upper secondary education students took part in our cross-sectional study. Structural equation modeling was used to analyze the association between empathy (i.e., cognitive and affective empathy), and study burnout and study engagement. The results showed that cognitive empathy contributed to affective empathy, which was further related to increased levels of study engagement, and decreased levels of cynicism, and sense of inadequacy. The role of cognitive empathy seemed to be more complicated: while cognitive empathy contributed directly to increased levels of cynicism, and inadequacy and decrease in study engagement, the indirect effects of cognitive empathy (through affective empathy) on cynicism and inadequacy were negative, and positive on study engagement. Neither of the empathy dimensions explained students' emotional exhaustion. The results indicate that merely teaching students to recognize and identify their peers' emotions is not sufficient to enhance study wellbeing, but they need to learn to share emotions and to tune into each other's emotions.
Keywords: adolescents; affective empathy; cognitive empathy; empathy; structural equation modeling; study burnout; study engagement.
Copyright © 2022 Tikkanen, Anttila, Pyhältö, Soini and Pietarinen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Alloway T. P., Copello E., Loesch M., Soares C., Watkins J., Miller D., et al. (2016). Investigating the reliability and validity of the multidimensional emotional empathy scale. Meas 90 438–442. 10.1016/j.measurement.2016.05.014 - DOI
-
- Baldner C., McGinley J. (2014). Correlational and exploratory factor analyses (EFA) of commonly used empathy questionnaires: New insights. Motiv. Emot. 38 727–744. 10.1007/s11031-014-9417-2 - DOI
-
- Bask M., Salmela-Aro K. (2013). Burned out to drop out: Exploring the relationship between school burnout and school dropout. Eur. J. Psychol. Educ. 28 511–528. 10.1007/s10212-012-0126-5 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

