Risk factors for postoperative delirium following total hip or knee arthroplasty: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 36248575
- PMCID: PMC9565976
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.993136
Risk factors for postoperative delirium following total hip or knee arthroplasty: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to identify risk factors for delirium after total joint arthroplasty (TJA) and provide theoretical guidance for reducing the incidence of delirium after TJA.
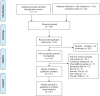
Methods: The protocol for this meta-analysis is registered with PROSPERO (CRD42020170031). We searched PubMed, the Cochrane Library and Embase for observational studies on risk factors for delirium after TJA. Review Manager 5.3 was used to calculate the relative risk (RR) or standard mean difference (SMD) of potential risk factors related to TJA. STATA 14.0 was used for quantitative publication bias evaluation.
Results: In total, 25 studies including 3,767,761 patients from 9 countries were included. Old age has been widely recognized as a risk factor for delirium. Our results showed that the main risk factors for delirium after TJA were patient factors (alcohol abuse: RR = 1.63; length of education: SMD = -0.93; and MMSE score: SMD = -0.39), comorbidities (hypertension: RR = 1.26; diabetes mellitus: RR = 1.67; myocardial infarction: RR = 17.75; congestive heart failure: RR = 2.54; dementia: RR = 17.75; renal disease: RR = 2.98; history of stroke: RR = 4.83; and history of mental illness: RR = 2.36), surgical factors (transfusion: RR = 1.53; general anesthesia: RR = 1.10; pre-operative albumin: SMD = -0.38; pre-operative hemoglobin: SMD = -0.29; post-operative hemoglobin: SMD = -0.24; total blood loss: SMD = 0.15; duration of surgery: SMD = 0.29; and duration of hospitalization: SMD = 2.00) and drug factors (benzodiazepine use: RR = 2.14; ACEI use: RR = 1.52; and beta-blocker use: RR = 1.62).
Conclusions: Multiple risk factors were associated with delirium after TJA. These results may help doctors predict the occurrence of delirium after surgery and determine the correct treatment.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier: CRD42020170031.
Keywords: meta-analysis; post-operative delirium; risk factor; systematic review; total joint arthroplasty.
Copyright © 2022 Zhao, Liang, Hong, Pan, Luo, Liu and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Incidence and associated factors of delirium after primary total joint arthroplasty in elderly patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 May 31;103(22):e38395. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038395. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39259060 Free PMC article.
-
Application of enhanced recovery after surgery in partial nephrectomy for renal tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2023 Feb 9;13:1049294. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1049294. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36845687 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of postoperative delirium in elderly patients following total hip and knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021 Nov 12;22(1):945. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04825-1. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021. PMID: 34772392 Free PMC article.
-
Protocol for a single-centre prospective observational study of postoperative delirium following total joint arthroplasties among South East Asians.BMJ Open. 2018 Mar 6;8(3):e019426. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-019426. BMJ Open. 2018. PMID: 29511014 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of risk factor for postoperative delirium following spinal surgery.J Orthop Surg Res. 2020 Nov 5;15(1):509. doi: 10.1186/s13018-020-02035-4. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 33153465 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Clinical biomarkers of perioperative neurocognitive disorder: initiation and recommendation.Sci China Life Sci. 2025 Jul;68(7):1912-1940. doi: 10.1007/s11427-024-2797-x. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Sci China Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 39918707 Review.
-
Risk factors and prediction model of delirium in elderly patients after hip arthroplasty.Pak J Med Sci. 2024 Jul;40(6):1077-1082. doi: 10.12669/pjms.40.6.9306. Pak J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38952533 Free PMC article.
-
Delirium after deep brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease: a meta-analysis of incidence and risk factors.Neurosurg Rev. 2025 Jan 23;48(1):73. doi: 10.1007/s10143-025-03206-9. Neurosurg Rev. 2025. PMID: 39843798
-
Retrospective comparison of the effects of remimazolam and dexmedetomidine on postoperative delirium in elderly patients undergoing orthopedic surgery of the lower extremities under spinal anesthesia.J Anesth. 2024 Dec;38(6):771-779. doi: 10.1007/s00540-024-03386-6. Epub 2024 Aug 25. J Anesth. 2024. PMID: 39182205
-
Risk factors for postoperative delirium in orthopaedic hip surgery patients: a database review.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Jan 17;25(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07174-x. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 38233831 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources