Plasma proteome responses in zebrafish following λ-carrageenan-Induced inflammation are mediated by PMN leukocytes and correlate highly with their human counterparts
- PMID: 36248846
- PMCID: PMC9559376
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1019201
Plasma proteome responses in zebrafish following λ-carrageenan-Induced inflammation are mediated by PMN leukocytes and correlate highly with their human counterparts
Abstract
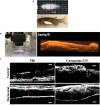
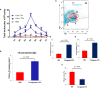
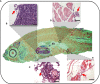
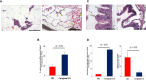
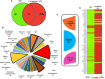
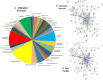
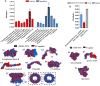
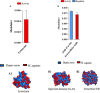
Regulation of inflammation is a critical process for maintaining physiological homeostasis. The λ-carrageenan (λ-CGN) is a mucopolysaccharide extracted from the cell wall of red algae (Chondrus crispus) capable of inducing acute intestinal inflammation, which is translated into the production of acute phase reactants secreted into the blood circulation. However, the associated mechanisms in vertebrates are not well understood. Here, we investigated the crucial factors behind the inflammatory milieu of λ-CGN-mediated inflammation administered at 0, 1.75, and 3.5% (v/w) by i.p. injection into the peritoneal cavity of adult zebrafish (ZF) (Danio rerio). We found that polymorphonuclear leukocytes (neutrophils) and lymphocytes infiltrating the ZF peritoneal cavity had short-term persistence. Nevertheless, they generate a strong pattern of inflammation that affects systemically and is enough to produce edema in the cavity. Consistent with these findings, cell infiltration, which causes notable tissue changes, resulted in the overexpression of several acute inflammatory markers at the protein level. Using reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography followed by a hybrid linear ion-trap mass spectrometry shotgun proteomic approach, we identified 2938 plasma proteins among the animals injected with PBS and 3.5% λ-CGN. First, the bioinformatic analysis revealed the composition of the plasma proteome. Interestingly, 72 commonly expressed proteins were recorded among the treated and control groups, but, surprisingly, 2830 novel proteins were differentially expressed exclusively in the λ-CGN-induced group. Furthermore, from the commonly expressed proteins, compared to the control group 62 proteins got a significant (p < 0.05) upregulation in the λ-CGN-treated group, while the remaining ten proteins were downregulated. Next, we obtained the major protein-protein interaction networks between hub protein clusters in the blood plasma of the λ-CGN induced group. Moreover, to understand the molecular underpinnings of these effects based on the unveiled protein sets, we performed a bioinformatic structural similarity analysis and generated overlapping 3D reconstructions between ZF and humans during acute inflammation. Biological pathway analysis pointed to the activation and abundance of diverse classical immune and acute phase reactants, several catalytic enzymes, and varied proteins supporting the immune response. Together, this information can be used for testing and finding novel pharmacological targets to treat human intestinal inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: Danio rerio (zebrafish); acute-phase proteins; glycoproteins; immunity; model organism; optical coherence tomography (OCT); proteomics; shotgun LC-MS/MS.
Copyright © 2022 Charlie-Silva, Feitosa, Pontes, Fernandes, Nóbrega, Gomes, Prata, Ferraris, Melo, Conde, Rodrigues, Aracati, Corrêa-Junior, Manrique, Superio, Garcez, Conceição, Yoshimura, Núñez, Eto, Fernandes, Freitas, Ribeiro, Nedoluzhko, Lopes-Ferreira, Borra, Barcellos, Perez, Malafaia, Cunha, Belo and Galindo-Villegas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular mechanism of action responsible for carrageenan-induced inflammatory response.Mol Immunol. 2019 May;109:38-42. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2019.02.020. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Mol Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30851635
-
Proteome dynamics in neutrophils of adult zebrafish upon chemically-induced inflammation.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014 Sep;40(1):217-24. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2014.06.035. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25014315
-
λ-carrageenan exacerbates Citrobacter rodentium-induced infectious colitis in mice by targeting gut microbiota and intestinal barrier integrity.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Dec;174:105940. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105940. Epub 2021 Oct 16. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 34666171
-
Food additive carrageenan: Part II: A critical review of carrageenan in vivo safety studies.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2014 Mar;44(3):244-69. doi: 10.3109/10408444.2013.861798. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24467586 Review.
-
Stressor-induced proteome alterations in zebrafish: a meta-analysis of response patterns.Aquat Toxicol. 2015 Feb;159:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.11.013. Epub 2014 Nov 27. Aquat Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 25498419 Review.
Cited by
-
Cyberlindnera jadinii yeast as a functional protein source: Modulation of immunoregulatory pathways in the intestinal proteome of zebrafish (Danio rerio).Heliyon. 2024 Feb 21;10(5):e26547. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26547. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38468924 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated transcriptomic and immune enzymatic analyses uncover coordinated immunometabolic responses in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) to Metanophrys sp. infection.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 16;16:1636453. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1636453. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40740775 Free PMC article.
-
Complement System Inhibitory Drugs in a Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Model: Computational Modeling.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 9;24(18):13895. doi: 10.3390/ijms241813895. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762197 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Farias WR, Nazareth RA, Mourão PA. Dual effects of sulfated d-galactans from the red algae botryocladia occidentalis preventing thrombosis and inducing platelet aggregation. Thromb Haemost (2001) 86:1540–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

