The cytokine network in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 36248849
- PMCID: PMC9554002
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1000996
The cytokine network in acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
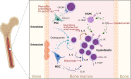
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a highly heterogeneous malignancy of the blood and bone marrow, characterized by clonal expansion of myeloid stem and progenitor cells and rapid disease progression. Chemotherapy has been the first-line treatment for AML for more than 30 years. Application of recent high-throughput next-generation sequencing technologies has revealed significant molecular heterogeneity to AML, which in turn has motivated efforts to develop new, targeted therapies. However, due to the high complexity of this disease, including multiple driver mutations and the coexistence of multiple competing tumorigenic clones, the successful incorporation of these new agents into clinical practice remains challenging. These continuing difficulties call for the identification of innovative therapeutic approaches that are effective for a larger cohort of AML patients. Recent studies suggest that chronic immune stimulation and aberrant cytokine signaling act as triggers for AML initiation and progression, facets of the disease which might be exploited as promising targets in AML treatment. However, despite the greater appreciation of cytokine profiles in AML, the exact functions of cytokines in AML pathogenesis are not fully understood. Therefore, unravelling the molecular basis of the complex cytokine networks in AML is a prerequisite to develop new therapeutic alternatives based on targeting cytokines and their receptors.
Keywords: acute myeloid leukemia; cytokine inhibitors; cytokine signaling; inflammation; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2022 Luciano, Krenn and Horejs-Hoeck.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pelcovits A, Niroula R. Acute myeloid leukemia: A review. Rhode Island Med J (2013) (2020) 103(3):38–40. - PubMed
-
- Noone AM HN, Krapcho M, Miller D, Brest A, Yu M, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z, Mariotto A, Lewis DR, Chen HS, Feuer EJ, Cronin KA. eds. SEER cancer statistics review, 1975-2015. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; (2018). Available at: https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2015/.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

