Targeting hypoxia-induced tumor stemness by activating pathogen-induced stem cell niche defense
- PMID: 36248858
- PMCID: PMC9559576
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.933329
Targeting hypoxia-induced tumor stemness by activating pathogen-induced stem cell niche defense
Abstract
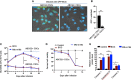
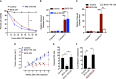
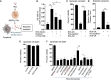
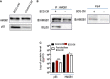
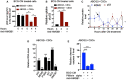
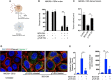
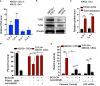
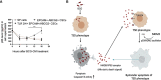
Tumor hypoxia and oxidative stress reprograms cancer stem cells (CSCs) to a highly aggressive and inflammatory phenotypic state of tumor stemness. Previously, we characterized tumor stemness phenotype in the ATP Binding Cassette Subfamily G Member 2 (ABCG2)-positive migratory side population (SPm) fraction of CSCs exposed to extreme hypoxia followed by reoxygenation. Here, we report that post-hypoxia/reoxygenation SPm+/ABCG2+ CSCs exerts defense against pathogen invasion that involves bystander apoptosis of non-infected CSCs. In an in vitro assay of cancer cell infection by Bacillus Calmette Guerin (BCG) or mutant Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) strain 18b (Mtb-m18b), the pathogens preferentially replicated intracellular to SPm+/ABCG2+ CSCs of seven cell lines of diverse cancer types including SCC-25 oral squamous cancer cell line. The conditioned media (CM) of infected CSCs exhibited direct anti-microbial activity against Mtb and BCG, suggesting niche defense against pathogen. Importantly, the CM of infected CSCs exhibited marked in vitro bystander apoptosis toward non-infected CSCs. Moreover, the CM-treated xenograft bearing mice showed 10- to 15-fold reduction (p < 0.001; n = 7) in the number of CSCs residing in the hypoxic niches. Our in vitro studies indicated that BCG-infected SPm+/ABCG2+ equivalent EPCAM+/ABCG2+ CSCs of SCC-25 cells underwent pyroptosis and released a high mobility group box protein 1 (HMGB1)/p53 death signal into the tumor microenvironment (TME). The death signal can induce a Toll-like receptor 2/4-mediated bystander apoptosis in non-infected CSCs by activating p53/MDM2 oscillation and subsequent activation of capase-3-dependent intrinsic apoptosis. Notably, SPm+/ABCG2+ but not SP cells undergoing bystander apoptosis amplified the death signal by further release of HMGB1/p53 complex into the TME. These results suggest that post-hypoxia SPm+/ABCG2+ CSCs serve a functional role as a tumor stemness defense (TSD) phenotype to protect TME against bacterial invasion. Importantly, the CM of TSD phenotype undergoing bystander apoptosis may have therapeutic uses against CSCs residing in the hypoxic niche.
Keywords: Altruistic Stem Cells (ASCs); Bacillus calmette guerin; Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs); Stem cell niche; Tumor hypoxia and oxidative stress microenvironment; Tumor stemness.
Copyright © 2022 Bhuyan, Pal, Pathak, Saikia, Mitra, Gayan, Mokhtari, Li, Ramana, Baishya and Das.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hypoxia-driven mobilization of altruistic cancer stem cells in platinum-treated head and neck cancer.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 3;15:1336882. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1336882. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39963656 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia enhances tumor stemness by increasing the invasive and tumorigenic side population fraction.Stem Cells. 2008 Jul;26(7):1818-30. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2007-0724. Epub 2008 May 8. Stem Cells. 2008. PMID: 18467664
-
Uncoupling Warburg effect and stemness in CD133+ve cancer stem cells from Saos-2 (osteosarcoma) cell line under hypoxia.Mol Biol Rep. 2018 Dec;45(6):1653-1662. doi: 10.1007/s11033-018-4309-2. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Mol Biol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30128626
-
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) in cancer progression and therapy.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jun;234(6):8381-8395. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27740. Epub 2018 Nov 11. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30417375 Review.
-
The Role of the Renin-Angiotensin System in the Cancer Stem Cell Niche.J Histochem Cytochem. 2021 Dec;69(12):835-847. doi: 10.1369/00221554211026295. Epub 2021 Jun 24. J Histochem Cytochem. 2021. PMID: 34165363 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic profiling reveals mechanism, therapeutic potential, and prognostic value of cancer stemness characteristic in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Mar 7;25(1):56. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01561-w. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40053129
-
Targeted Therapy of Tumors and Cancer Stem Cells based on Oxidant-regulated Redox Pathway and its Mechanism.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2025;21(4):425-440. doi: 10.2174/0115734099299174240522115944. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2025. PMID: 38818918 Review.
-
The emerging role of oral microbiota in oral cancer initiation, progression and stemness.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 26;14:1198269. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1198269. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37954619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune modulatory stem cells represent a significant component of the immune system.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 3;16:1543495. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1543495. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40098974 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Exploring beyond Common Cell Death Pathways in Oral Cancer: A Systematic Review.Biology (Basel). 2024 Feb 6;13(2):103. doi: 10.3390/biology13020103. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38392321 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

