SARS-CoV-2 antibody responses before and after a third dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine in Italian healthcare workers aged ≤60 years: One year of surveillance
- PMID: 36248864
- PMCID: PMC9566572
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.947187
SARS-CoV-2 antibody responses before and after a third dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine in Italian healthcare workers aged ≤60 years: One year of surveillance
Abstract
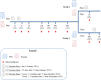
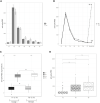
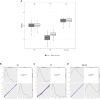
This study monitored the anti-spike-receptor-binding domain (RBD) and neutralizing antibodies induced by the Pfizer/BioNTech mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine in a cohort of 163 healthcare workers aged ≤60 years. We have taken advantage of two study groups, both of whom received the first two doses in the same time window, but Group 1 (54 HCWs) received the third dose 2 months before Group 2 (68 HCWs) did. The cohorts were monitored from the 12th day after the first vaccine dose up to 1 month after the third vaccine dose for a total of eight time points and about 1 year of surveillance (T1 = 12 days after the first dose; T2 = 10 days after the second dose; T3 = 1 month after the second dose; T4 = 3 months after the second dose; T5 = 4 months after the second dose; T6 = 5 months after the second dose; T7 = 7 months after the second dose; T8 = 1 month after the third dose for Group 1; T8* = 9 months after the second dose for Group 2; T9 = 1 month after the third dose for Group 2). The mean value of anti-spike antibodies decreased faster over time, but at T7, its decline was significantly slowed (T7 vs. T8*). After the third dose, the anti-spike titer rose about 34-fold (T7 vs. T8 and T8* vs. T9) and the booster improved the anti-spike titer by about three times compared with that of the second dose (T3 vs. T8 and T3 vs. T9), and no difference was noted between the two groups. The neutralizing titer was evaluated at T3, T7, T8, and T9. Anti-spike and neutralizing antibodies were found to be strongly correlated (r2 = 0.980; p < 0.001). At T3, 70% of the participants had a neutralizing antibody titer >91% of total anti-spike antibodies that increased to 90% after the third dose (T8 and T9). However, when the anti-spike titer reached its lowest value (T7), the neutralizing antibody levels decreased even further, representing only 44% of total anti-spike antibodies (p < 0.0001). Our findings show that the third vaccine dose improves the humoral response, but the wane of the anti-spike and neutralizing antibody titers over time is more marked in the neutralizing antibodies.
Keywords: BNT162b2; SARS-CoV-2; booster; humoral response; neutralizing antibodies; vaccine.
Copyright © 2022 Franzese, Coppola, Silva, Santini, Cinquanta, Ottomano, Salvatore and Incoronato.
Conflict of interest statement
Author SS is employed by Synlab Lazio Srl. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long follow-up of BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in healthcare workers (2020-2022): A retrospective longitudinal SARS-CoV-2 serological surveillance.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023 Aug;19(2):2258632. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2258632. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023. PMID: 37724517 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics and Persistence of the Cellular and Humoral Immune Responses to BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine in SARS-CoV-2-Naive and -Experienced Subjects: Impact of Booster Dose and Breakthrough Infections.Front Immunol. 2022 May 31;13:863554. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.863554. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35711445 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of humoral and cellular response to three doses of anti-SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 vaccine in patients with hematological malignancies and older subjects.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 26;14:1221587. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1221587. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38343436 Free PMC article.
-
The role of neutralizing antibodies by sVNT after two doses of BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in a cohort of Italian healthcare workers.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2022 Mar 17;60(6):934-940. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2022-0170. Print 2022 May 25. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2022. PMID: 35303766
-
Comparison of Antibody Response Elicited by ChAdOx1 and BNT162b2 COVID-19 Vaccine.J Korean Med Sci. 2021 Nov 29;36(46):e311. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e311. J Korean Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34845875 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 Specific Humoral Immune Responses after BNT162b2 Vaccination in Hospital Healthcare Workers.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Nov 29;10(12):2038. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10122038. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36560450 Free PMC article.
-
Neutralizing Antibody Response following a Third Dose of the mRNA-1273 Vaccine among Cancer Patients.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Dec 22;12(1):13. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12010013. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38250826 Free PMC article.
-
Early Immune Cell and Antibody Kinetics Following SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Healthy Adults and Low-Count Monoclonal B-Cell Lymphocytosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 15;26(2):681. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020681. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859394 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of Synlab SDN Biobank's quality control system.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 20;14(1):19303. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70263-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39164464 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of residual humoral immune response against SARS-CoV-2 by a surrogate virus neutralization test (sVNT) 9 months after BNT162b2 primary vaccination.J Infect Chemother. 2023 Jun;29(6):624-627. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2023.03.002. Epub 2023 Mar 11. J Infect Chemother. 2023. PMID: 36914095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haas EJ, Angulo FJ, McLaughlin JM, Anis E, Singer SR, Khan F, et al. . Impact and effectiveness of mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 infections and COVID-19 cases, hospitalisations, and deaths following a nationwide vaccination campaign in Israel: An observational study using national surveillance data. Lancet (2021) 397:1819–29. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(21)00947-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

