Comparative efficacy and safety of JAK inhibitors as monotherapy and in combination with methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36248913
- PMCID: PMC9556706
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.977265
Comparative efficacy and safety of JAK inhibitors as monotherapy and in combination with methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: We aim to evaluate the efficacy and tolerability of Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi) as monotherapy and in combination with methotrexate (MTX) in active rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
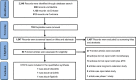
Methods: Medline, EMBASE, and Cochrane Library were systematically searched to identify relevant randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Pooled analysis was conducted using random-effects model, along with the risk difference (RD) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
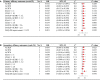
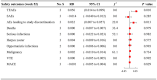
Results: Three RCTs, including 2,290 patients, were included. JAKi (tofacitinib, baricitinib, and filgotinib) plus MTX displayed a higher proportion of patients meeting the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria than JAKi alone at week 52 (ACR20 RD 0.032; 95% CI -0.027 to 0.091; ACR50 RD 0.050; 95% CI 0.003 to 0.097; ACR70 RD 0.056; 95% CI 0.012 to 0.100). Similar results were observed for ACR20/50/70 at week 24. No significant difference was found between two regimens for the proportion of patients achieving Health Assessment Questionnaire disability index (HAQ-DI) improvement ≥ 0.22 at weeks 24 and 52. Regarding low disease activity and remission achievement, JAKi in combination with MTX, contributed higher response rates than JAKi alone at weeks 24 and 52. Compared with JAKi monotherapy, combination therapy had a higher risks of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) and adverse events (AEs) leading to study discontinuation.
Conclusion: JAKi combined with MTX demonstrated superiority to JAKi monotherapy in terms of ACR responses, low disease activity and remission achievement. The two regimens presented comparable physical functioning measured by HAQ-DI improvement and similar tolerability, except for high risks of TEAEs and AEs leading to study discontinuation in combination therapy.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/, identifier CRD42021288907.
Keywords: combination therapy; janus kinase inhibitors; methotrexate; monotherapy; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Yan, Shi, Lin, Gu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative study of the efficacy and safety of tofacitinib, baricitinib, upadacitinib, and filgotinib versus methotrexate for disease-modifying antirheumatic drug-naïve patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Z Rheumatol. 2021 Nov;80(9):889-898. doi: 10.1007/s00393-020-00889-x. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Z Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 32970188 English.
-
Relative efficacy and safety of tofacitinib, baricitinib, upadacitinib, and filgotinib in comparison to adalimumab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis.Z Rheumatol. 2020 Oct;79(8):785-796. doi: 10.1007/s00393-020-00750-1. Z Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32055928 English.
-
Effectiveness and Safety of Iguratimod Monotherapy or Combined With Methotrexate in Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 5;13:911810. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.911810. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35991879 Free PMC article.
-
Baricitinib, Methotrexate, or Combination in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis and No or Limited Prior Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drug Treatment.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017 Mar;69(3):506-517. doi: 10.1002/art.39953. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 27723271 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative efficacy of five approved Janus kinase inhibitors as monotherapy and combination therapy in patients with moderate-to-severe active rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 24;15:1387585. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1387585. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38725657 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Janus kinase inhibitors and methotrexate on interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis patients.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 16;15:1501146. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1501146. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39737175 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Real-World Evidence to Assess Effectiveness Outcomes of Janus Kinase Inhibitors for Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review of US Studies.Drug Healthc Patient Saf. 2025 Jan 7;17:25-49. doi: 10.2147/DHPS.S492887. eCollection 2025. Drug Healthc Patient Saf. 2025. PMID: 39802749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety of JAK and IL-6 inhibitors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a multicenter cohort study.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 2;14:1267749. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1267749. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37868999 Free PMC article.
-
Tanshinone IIA, a component of the self-made Xiao-Yin decoction, ameliorates psoriasis by inhibiting IL-17/IL-23 and PTGS2/NF-κB/AP-1 pathways.Skin Res Technol. 2024 Feb;30(2):e13577. doi: 10.1111/srt.13577. Skin Res Technol. 2024. PMID: 38284293 Free PMC article.
-
Nanotechnology-empowered combination therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: principles, strategies, and challenges.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Jul 22;22(1):431. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02670-7. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39034407 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Smolen JS, Landewé RBM, Bijlsma JWJ, Burmester GR, Dougados M, Kerschbaumer A, et al. . EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann rheumatic Dis (2020) 79(6):685–99. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216655 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Burmester GR, Blanco R, Charles-Schoeman C, Wollenhaupt J, Zerbini C, Benda B, et al. . Tofacitinib (CP-690,550) in combination with methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis with an inadequate response to tumour necrosis factor inhibitors: A randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet (London England) (9865) 2013:451–60:381. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61424-X - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

