PEX6 Mutations in Peroxisomal Biogenesis Disorders: An Usher Syndrome Mimic
- PMID: 36249295
- PMCID: PMC9559095
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xops.2021.100028
PEX6 Mutations in Peroxisomal Biogenesis Disorders: An Usher Syndrome Mimic
Abstract
Purpose: Peroxisomal biogenesis disorders (PBDs) represent a spectrum of conditions that result in vision loss, sensorineural hearing loss, neurologic dysfunction, and other abnormalities resulting from aberrant peroxisomal function caused by mutations in PEX genes. With no treatments currently available, we sought to investigate the disease mechanism in a patient with a PBD caused by defects in PEX6 and to probe whether overexpression of PEX6 could restore peroxisome function and potentially offer therapeutic benefit.
Design: Laboratory-based study.
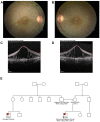
Participants: A 12-year-old boy sought treatment with hearing loss and retinopathy. After negative results in an Usher syndrome panel, targeted genetic testing revealed compound heterozygous mutations in PEX6. These included a 14-nucleotide deletion (c.802_815del: p.(Asp268Cysfs∗8)) and a milder missense variant (c.35T→C:(p.Phe12Ser)).
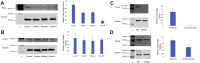
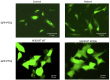
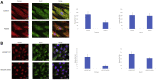
Methods: Patient-derived skin fibroblasts were cultured, and a PEX6 knockout cell line was developed using clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats and Cas9 technology in HEK293T cells to emulate a more severe disease phenotype. Immunoblot analysis of whole cell lysates was performed to assess peroxisome number. Immunofluorescence studies used antibodies against components of the peroxisomal protein import pathway to interrogate the effects of mutations in PEX6 on protein trafficking.
Main outcome measures: Primary outcome measures were peroxisome abundance and matrix protein import.
Results: Peroxisome number was not significantly different between control fibroblasts and patient fibroblasts; however, fewer peroxisomes were observed in PEX6 knockout cells compared with wild-type cells (P = 0.04). Analysis by immunofluorescent microscopy showed significantly impaired peroxisomal targeting signal 1- and peroxisomal targeting signal 2-mediated matrix protein import in both patient fibroblasts and PEX6 knockout cells. Overexpressing PEX6 resulted in improved matrix protein import in PEX6 knockout cells.
Conclusions: Mutations in PEX6 were responsible for combined hearing loss and retinopathy in our patient. The primary peroxisomal defect in our patient's skin fibroblasts was impaired peroxisomal protein import as opposed to reduction in the number of peroxisomes. Genetic strategies that introduce wild-type PEX6 into cells deficient in PEX6 protein show promise in restoring peroxisome function. Future studies of patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cell-derived retinal pigment epithelium cells may clarify the role of PEX6 in the retina and the potential for gene therapy in these patients.
Keywords: CRISPR, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats; DTM, docking translocation module; GFP, green fluorescent protein; HEK293T, human embryonic kidney 293T; Hearing loss; PBD, peroxisomal biogenesis disorder; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; PEX6; PTS1, peroxisomal targeting signal 1; PTS2, peroxisomal targeting signal 2; Peroxisomal biogenesis disorders; Peroxisome; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; Retinal degeneration; Usher syndrome; WT, wild-type.
© 2021 by the American Academy of Ophthalmology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of three distinct peroxisomal protein import defects in patients with peroxisome biogenesis disorders.J Cell Sci. 1995 May;108 ( Pt 5):1817-29. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.5.1817. J Cell Sci. 1995. PMID: 7544797
-
Metabolic control of peroxisome abundance.J Cell Sci. 1999 May;112 ( Pt 10):1579-90. doi: 10.1242/jcs.112.10.1579. J Cell Sci. 1999. PMID: 10212151
-
Alternative splicing suggests extended function of PEX26 in peroxisome biogenesis.Am J Hum Genet. 2005 Jun;76(6):987-1007. doi: 10.1086/430637. Epub 2005 Apr 27. Am J Hum Genet. 2005. PMID: 15858711 Free PMC article.
-
Pexophagy is responsible for 65% of cases of peroxisome biogenesis disorders.Autophagy. 2017 May 4;13(5):991-994. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2017.1291480. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Autophagy. 2017. PMID: 28318378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular basis of peroxisomal biogenesis disorders caused by defects in peroxisomal matrix protein import.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Sep;1822(9):1326-36. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.05.010. Epub 2012 May 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22617146 Review.
Cited by
-
Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Pathogenesis Underlying Inherited Retinal Dystrophies.Biomolecules. 2023 Feb 1;13(2):271. doi: 10.3390/biom13020271. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36830640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Addis Ababa Lions: Whole-Genome Sequencing of a Rare and Precious Population.Genome Biol Evol. 2024 Feb 1;16(2):evae021. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evae021. Genome Biol Evol. 2024. PMID: 38302110 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Potential Feature Genes in CRSwNP Using Bioinformatics Analysis and Machine Learning Strategies.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Oct 22;17:7573-7590. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S484914. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39464338 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fujiki Y., Abe Y., Imoto Y., et al. Recent insights into peroxisome biogenesis and associated diseases. J Cell Sci. 2020;133(9):jcs236943. - PubMed
-
- Mast F.D., Fagarasanu A., Knoblach B., Rachubinski R.A. Peroxisome biogenesis: something old, something new, something borrowed. Physiology (Bethesda) 2010;25(6):347–356. - PubMed
-
- Di Cara F., Sheshachalam A., Braverman N.E., et al. Peroxisome-mediated metabolism is required for immune response to microbial infection. Immunity. 2017;47(1):93–106. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

