Comparison of dexmedetomidine and remifentanil on reducing coughing during emergence from anesthesia with tracheal intubation: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 36249748
- PMCID: PMC9561905
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.993239
Comparison of dexmedetomidine and remifentanil on reducing coughing during emergence from anesthesia with tracheal intubation: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Dexmedetomidine and remifentanil are well known to suppress airway reflex during emergence from anesthesia, but which one is more effective is unclear. We conducted a meta-analysis to compare the effect of dexmedetomidine and remifentanil on reducing the occurrence of coughing. Methods: We systematically searched PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library for randomized controlled trials (published between 1 January 1950, and 30 December 2021; no language restrictions) comparing dexmedetomidine infusion with remifentanil infusion. The primary endpoint was the incidence of moderate to severe coughing during the recovery period. The secondary endpoints were the time of recovery and extubation, and residual sedation. We assessed pooled data by using a random-effects model. Results: Eight studies with 502 participants were included. The meta-analysis showed no statistically difference between dexmedetomidine and remifentanil in the occurrence of moderate to severe coughing during emergence from anesthesia (OR 1.45,95%CI 0.62-3.38), the extubation time (MD 0.93 min, 95%CI -0.28-2.14), and the residual sedation (OR 2.52, 95%CI 0.92-6.91). Compared with dexmedetomidine, the average recovery time of remifentanil was shorter (MD 3.88 min, 95%CI 1.01-6.75). Conclusion: Dexmedetomidine and remifentanil infusion had no difference in the occurrence of moderate to severe coughing during emergence from anesthesia. Clinical Trial Registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/, identifier CRD42021239710.
Keywords: dexmedetomidine; emergence coughing; extubation; general anaesthesia; remifentanil.
Copyright © 2022 Fan, Cai, Pan and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




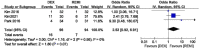
References
-
- Chen J. W., Lv X., Zhang L., Chen Z. F. (2016). Effects of remifentanil and dexmedetomidine on recovery profiles after oral and maxillofacial surgery. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue 25 (1), 101–104. - PubMed
-
- Choi E. K., Kwon N., Park S. J. (2018). Comparison of the effects of oxycodone versus fentanyl on airway reflex to tracheal extubation and postoperative pain during anesthesia recovery after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A double-blind, randomized clinical consort study. Medicine 97 (13), e0156. 10.1097/md.0000000000010156 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

