Imbalance of helper T cell type 1, helper T cell type 2 and associated cytokines in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 36249802
- PMCID: PMC9556996
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.988512
Imbalance of helper T cell type 1, helper T cell type 2 and associated cytokines in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A meta-analysis
Abstract
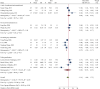
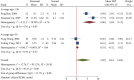
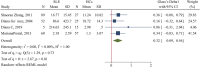
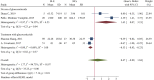
Objective: Th1 and Th2 cells and their associated cytokines function in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), but their exact roles are uncertain. We performed a meta-analysis to examine the relationship of these cells and cytokines with SLE. Methods: Multiple databases were searched to identify publications that reported the percentages of Th1 and Th2 cells and their associated cytokines in SLE patients and healthy controls (HCs). Meta-analysis was performed using Stata MP version 16. Results: SLE patients had a lower percentage of Th1 cells, a higher percentage of Th2 cells, and higher levels of Th1- and Th2-associated cytokines than HCs. SLE treatments normalized some but not all of these indicators. For studies in which the proportion of females was less than 94%, the percentage of Th2 cells and the level of IL-10 were higher in patients than HCs. SLE patients who had abnormal kidney function and were younger than 30 years old had a higher proportion of Th1 cells than HCs. SLE patients more than 30 years old had a higher level of IL-6 than HCs. Conclusion: Medications appeared to restore the balance of Th1 cells and other disease indicators in patients with SLE. Gender and age affected the levels of Th1 and Th2 cells, and the abnormally elevated levels of Th2 cells appear to be more pronounced in older patients and males. Systematic Review Registration: [https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/], identifier [CRD42022296540].
Keywords: cytokines; helper T cell type 1; helper T cell type 2; meta-analysis; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2022 Xiang, Zhang, Zhang, Qian, Wang, Wang, Xiang and Ding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Imbalance of Th17 cells, Treg cells and associated cytokines in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 17;15:1425847. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1425847. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39086480 Free PMC article.
-
BAFF-R and TACI expression on CD3+ T cells: Interplay among BAFF, APRIL and T helper cytokines profile in systemic lupus erythematosus.Cytokine. 2019 Feb;114:115-127. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.11.008. Epub 2018 Nov 19. Cytokine. 2019. PMID: 30467093
-
Elevated gene expression of Th1/Th2 associated transcription factors is correlated with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.J Rheumatol. 2007 Jan;34(1):89-96. Epub 2006 Nov 15. J Rheumatol. 2007. PMID: 17117487
-
Th1/Th2/Th17/Treg cytokine imbalance in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients: Correlation with disease activity.Cytokine. 2015 Apr;72(2):146-53. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2014.12.027. Epub 2015 Jan 31. Cytokine. 2015. PMID: 25647269
-
Systematic literature review on early clinical evidence for immune-resolution therapies and potential benefits to patients and healthcare providers.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 17;15:1425478. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1425478. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39483464 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
sNASP Mutation Aggravates to the TLR4-Mediated Inflammation in SLE by TAK1 Pathway.J Immunol Res. 2023 Sep 20;2023:4877700. doi: 10.1155/2023/4877700. eCollection 2023. J Immunol Res. 2023. PMID: 37771504 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphocytes Change Their Phenotype and Function in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 10;25(20):10905. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010905. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism and application of mesenchymal stem cells and their secreting extracellular vesicles in regulating CD4+T cells in immune diseases.Biophys Rep. 2024 Dec 31;10(6):403-415. doi: 10.52601/bpr.2024.240005. Biophys Rep. 2024. PMID: 39758422 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging Lymphatic System Targeting in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus for Improved Clinical Outcomes.Pharmacol Rev. 2024 Feb 13;76(2):228-250. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.123.000938. Pharmacol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38351070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Modulate Cytokine Secretion of CD4+ T Cell in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus by Inhibiting HSP90AA1 in the Glucose-Activated PI3K-AKT Pathway.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2025 Aug;13(8):e70239. doi: 10.1002/iid3.70239. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2025. PMID: 40801323 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

