Phenotypic and molecular responses of copepods to UV radiation stress in a clear versus a glacially turbid lake
- PMID: 36249915
- PMCID: PMC9543624
- DOI: 10.1111/fwb.13953
Phenotypic and molecular responses of copepods to UV radiation stress in a clear versus a glacially turbid lake
Abstract
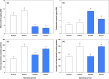
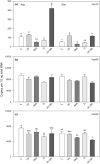
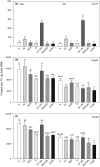
Zooplankton are exposed to multiple environmental stressors in alpine lakes. However, phenotypic and molecular responses of copepods to different environmental conditions, including ultraviolet radiation (UVR), are still not fully understood. Here, we tested whether gene expression patterns vary within the same species, Cyclops abyssorum tatricus, but in populations from different environments (a clear vs. a glacially turbid lake) when exposed to UVR. Moreover, we wanted to examine potential seasonal variation (summer vs. autumn) in copepod gene expression.We measured photoprotective compounds (mycosporine-like amino acids and carotenoids) and antioxidant capacities in two copepod populations and studied gene expression of heat shock proteins (hsps) as indicator of stress after UVR exposure in the laboratory.Compared with the copepod population from the clear lake, the population from the turbid lake showed lower mycosporine-like amino acid, but higher carotenoid concentrations that decreased over the season. Antioxidant capacities (both lipophilic and hydrophilic) were higher in autumn than in summer. The hsp60 and hsp90 genes were constitutively expressed, regardless of habitat origin and season, while hsp70 was upregulated after exposure to UVR (up to 2.8-fold change). We observed stronger upregulation of hsp70 gene expression in autumn for the turbid and summer for the clear lake, with highest gene expression 24 hr post-UVR exposure (up to 10.2-fold change in the turbid and 3.9-fold in the clear lake).We show how variation in phenotypic traits modulates hsp gene expression patterns, specifically hsp70 gene expression. Rapidly induced defences against cellular stress may improve survival in harsh environments such as alpine lakes, especially since these sensitive ecosystems may experience further changes in the future.
Keywords: alpine lakes; glacier retreat; hsp70; photoprotection; zooplankton.
© 2022 The Authors. Freshwater Biology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Seasonal plasticity in photoprotection modulates UV-induced hsp gene expression in copepods from a clear lake.Limnol Oceanogr. 2018 Jul;63(4):1579-1592. doi: 10.1002/lno.10793. Epub 2018 Feb 16. Limnol Oceanogr. 2018. PMID: 30333668 Free PMC article.
-
UV-induced DNA damage in Cyclops abyssorum tatricus populations from clear and turbid alpine lakes.J Plankton Res. 2014 Mar;36(2):557-566. doi: 10.1093/plankt/fbt109. Epub 2013 Nov 11. J Plankton Res. 2014. PMID: 24616551 Free PMC article.
-
Contrasting diurnal patterns in antioxidant capacities, but not in expression of stress protein genes among copepod populations from clear versus glacially fed alpine and subalpine lakes.J Plankton Res. 2019 Nov;41(6):897-908. doi: 10.1093/plankt/fbz061. Epub 2019 Dec 10. J Plankton Res. 2019. PMID: 31920209 Free PMC article.
-
Mycosporine-Like Amino Acids (MAAs) in Zooplankton.Mar Drugs. 2020 Jan 23;18(2):72. doi: 10.3390/md18020072. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 31979234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mycosporine-Like Amino Acids: Making the Foundation for Organic Personalised Sunscreens.Mar Drugs. 2019 Nov 12;17(11):638. doi: 10.3390/md17110638. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31726795 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adrian, R. , O'Reilly, C. M. , Zagarese, H. , Baines, S. B. , Hessen, D. O. , Keller, W. , Livingstone, D. M. , Sommaruga, R. , Straile, D. , van Donk, E. , Weyhenmeyer, G. A. , & Winder, M. (2009). Lakes as sentinels of climate change. Limnology Oceanography, 54(6), 2283–2297. 10.4319/lo.2009.54.6_part_2.2283 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alonso, C. , Rocco, V. , Barriga, J. P. , Battini, M. A. , & Zagarese, H. (2004). Surface avoidance by freshwater zooplankton: Field evidence on the role of ultraviolet radiation. Limnology Oceanography, 49(1), 225–232. 10.4319/lo.2004.49.1.0225 - DOI
-
- Andersson, M. , Van Nieuwerburgh, L. , & Snoeijs, P. (2003). Pigment transfer from phytoplankton to zooplankton with emphasis on astaxanthin production in the Baltic Sea food web. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 254, 213–224. 10.3354/meps254213 - DOI
-
- Arendt, K. E. , Dutz, J. , Jónasdóttir, S. H. , Jung‐Madsen, S. , Mortensen, J. , Møller, E. F. , & Nielsen, T. G. (2011). Effects of suspended sediments on copepods feeding in a glacial influenced sub‐Arctic fjord. Journal of Plankton Research, 33(10), 1526–1537. 10.1093/plankt/fbr054 - DOI
-
- Bligh, E. G. , & Dyer, W. J. (1959). A rapid method for total lipid extraction and purification. Canadian Journal Biochemistry Physiology, 37(8), 911–917. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
