Fiber-enriched botanicals: A therapeutic tool against certain metabolic ailments
- PMID: 36249968
- PMCID: PMC9548355
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.2920
Fiber-enriched botanicals: A therapeutic tool against certain metabolic ailments
Abstract
Plant-based foods are natural sources including vegetables, fruits, cereals and legumes. These foods consist of various types of nutrients in which carbohydrate is the basic component. However, some plant-based diets contain carbohydrates in the form of fiber. The fiber is usually a nondigestible polysaccharide that is not digested in the human body. It is present in the form of soluble or insoluble in different part of foods like peel, bran, pulp and grain. Pectin, beta-glucan, mucilage, psyllium, resistant starch and inulin are soluble fiber, and cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin are insoluble fiber attained from plant foods. The major function enhances immunity by creating gastrointestinal barrier, mucus production, immune cell activity and IgA level. Previous evidences showed that peoples with strong immunity have fewer chances of viral disease. A recent viral disease named COVID-19 spread in the world and millions of peoples died due to this viral disease. Coronavirus mostly attacks humans that suffer with weak immune system. It is due chronic diseases like diabetes and CVD (cardiovascular disease). The current review shows that fiber-containing plant-based foods boost immunity and aid human against COVID-19. The therapeutic role of fiber in the human body is to control the risk of hypertension and diabetes because a high-fiber diet has the ability to lower cholesterol, blood pressure and blood sugar. Fibers aid in GIT (gastrointestinal tract) and prevent constipation because it absorbs water and adds bulk to stool.
Keywords: COVID‐19; diseases; fiber; immune system; plant‐based foods.
© 2022 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures
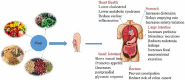
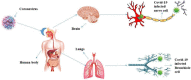
Similar articles
-
Dietary Fiber, Atherosclerosis, and Cardiovascular Disease.Nutrients. 2019 May 23;11(5):1155. doi: 10.3390/nu11051155. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31126110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the Physics of Functional Fibers in the Gastrointestinal Tract: An Evidence-Based Approach to Resolving Enduring Misconceptions about Insoluble and Soluble Fiber.J Acad Nutr Diet. 2017 Feb;117(2):251-264. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2016.09.021. Epub 2016 Nov 15. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2017. PMID: 27863994 Review.
-
Cereal grains, legumes and diabetes.Eur J Clin Nutr. 2004 Nov;58(11):1443-61. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601995. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2004. PMID: 15162131 Review.
-
Beyond Insoluble Dietary Fiber: Bioactive Compounds in Plant Foods.Nutrients. 2023 Sep 25;15(19):4138. doi: 10.3390/nu15194138. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37836422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary Fibers in Healthy Children and in Pediatric Gastrointestinal Disorders: A Practical Guide.Nutrients. 2023 May 6;15(9):2208. doi: 10.3390/nu15092208. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37432354 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The effects of specific vegetable subtypes on constipation incidence in the general United States population.Front Nutr. 2024 Jul 24;11:1403636. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1403636. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39114125 Free PMC article.
-
Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Different Vegetable Sprouts and Their Potential Role in the Formulation of Functional Foods against Various Disorders: A Literature-Based Review.Molecules. 2022 Oct 28;27(21):7320. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217320. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Chronic Laxative Use on Lipid Profile and HbA1c: A Hospital-Based Retrospective Study.Cureus. 2023 Sep 11;15(9):e45055. doi: 10.7759/cureus.45055. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37829969 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Consuming Heat-Treated Dodamssal Brown Rice Containing Resistant Starch on Glucose Metabolism in Humans.Nutrients. 2023 May 9;15(10):2248. doi: 10.3390/nu15102248. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37242130 Free PMC article.
-
The Significance of Plant Nutrition in the Creation of the Intestinal Microbiota-Prevention of Chronic Diseases: A Narrative Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Nov 29;60(12):1969. doi: 10.3390/medicina60121969. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39768848 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aleixandre, A. , & Miguel, M. (2016). Dietary fiber and blood pressure control. Food & Function, 7(4), 1864–1871. - PubMed
-
- Alonso‐Coello, P. , Mills, E. D. , Heels‐Ansdell, D. , Lopez‐Yarto, M. , Zhou, Q. I. , Johanson, J. F. , & Guyatt, G. (2006). Fiber for the treatment of hemorrhoids complications: A systematic review and meta‐analysis. American Journal of Gastroenterology, 101(1), 181–188. - PubMed
-
- AL‐Rawi, M. M. (2007). Efficacy of oat bran (Avena sativa L.) in comparison with atorvastatin in treatment of hypercholesterolemia in albino rat liver. The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine, 29(1), 511–521.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

