Hordeum vulgare L. microgreen mitigates reproductive dysfunction and oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetes and aflatoxicosis in male rats
- PMID: 36249986
- PMCID: PMC9548372
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.2936
Hordeum vulgare L. microgreen mitigates reproductive dysfunction and oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetes and aflatoxicosis in male rats
Abstract
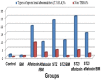
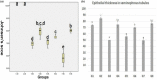
Diabetes mellitus type 2 (DM) is a common chronic disease worldwide, which may be due to increased environmental pollution. Aflatoxin B1 is a likely inevitable contaminant in food and dairy products. Both DM and aflatoxicosis exert a deleterious effect on reproduction urging the exploration of various functional food for protection. This study investigated the effect of barley microgreen (BM) on reproductive disorders caused by DM with or without aflatoxicosis in male rats. Rats were divided into eight groups; G1 control, G2 barley, G3 aflatoxin, G4 aflatoxin-barley, G5 streptozotocin (STZ), G6 STZ-barley, G7 STZ-aflatoxin, and G8 STZ-aflatoxin-barley. BM chemical composition revealed elevated calcium, iron, phosphorus, and vitamin A compared with barely seeds. Complete blood picture, lipid profile, serum oxidative stress parameters, relative testicular weight, sperm analysis, chromosomal aberration, and testis histopathology were performed. The lipid profile was altered significantly in G7. Oxidative stress was increased in G3, G5, and G7, whereas it was decreased in BM-treated groups. Sperm counts were reduced significantly in aflatoxin and/or STZ groups but increased significantly in BM-treated groups. Sperm morphological abnormalities and chromosomal aberrations were decreased significantly in BM-treated groups compared with untreated groups. Testicular histopathology revealed moderate diffuse degeneration of seminiferous tubules in aflatoxin and/or STZ groups, which were alleviated in BM-treated groups. In conclusion, aflatoxin and STZ together caused severe reproductive disorder and oxidative stress more than aflatoxin or STZ alone. BM diet reduced significantly oxidative stress and reproductive disorder associated with DM and aflatoxicosis in rats.
Keywords: aflatoxin; barley; chromosomal aberration histopathology; diabetes; sperm analysis.
© 2022 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures


References
-
- Abd El‐Aziem, S. H. , Mahrous, K. F. , Abdel‐Wahab, M. A. , Mahmoud, A. M. , & Hassan, A. M. (2004). Chemoprevention of barley and sage against acrylamide‐induced genotoxic, biochemical and histopathological alterations in rats. The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine, 15, 40–56. https://ejhm.journals.ekb.eg/article_18185.html
-
- Abdallah, M. M. F. (2008). Seed sprouts, a pharaoh’s heritage to improve food quality. Arab Universities Journal of Agriculture Science, 16, 469–478.
-
- Abdelatty, A. M. , Badr, O. A. M. , Mohamed, S. A. , Khattab, M. S. , Dessouki, S. M. , Farid, O. A. A. , Elolimy, A. A. , Sakr, O. G. , Elhady, M. A. , Mehesen, G. , & Bionaz, M. (2020). Long term conjugated linoleic acid supplementation modestly improved growth performance but induced testicular tissue apoptosis and reduced sperm quality in male rabbit. PLoS One, 15(1), e0226070. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abdel‐Gabbar, M. (2008). Effect of barley (Hordeum vulgare) on the liver of diabetic rats: Histological and biochemical study. Egypt Journal of Histology, 31, 245–255.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

