International taxation sentiment and COVID-19 crisis
- PMID: 36250041
- PMCID: PMC9540686
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ribaf.2022.101783
International taxation sentiment and COVID-19 crisis
Abstract
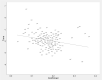
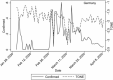
Investigating public sentiment regarding tax policy during the COVID-19 pandemic could be useful for understanding the experiences across societies. Using Linguistic Inquiry and Word Count to investigate and quantitatively measure the pandemic's effect-from January 25 to April 9, 2020-on the sentiment regarding possible tax policies throughout the world, thereby determining that, overall, taxation sentiment is reduced as the number of confirmed COVID-19 cases grows. Further investigation reveals that, as COVID-19 spreads, the sentiment for raising taxes decreases and that for reducing taxes increases, and this effect is mitigated by countries' democracy. We further find that news sentiment in unofficial media and in countries with low social trust is more significantly affected by COVID-19. Robustness tests performed using different subsamples of developed and developing countries and different pandemic circumstances validate our findings. This research has crucial implications for policy evaluation and development.
Keywords: COVID-19; Democratic accountability; Sentiment; Taxation.
© 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Public Sentiment and Discourse on Domestic Violence During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Australia: Analysis of Social Media Posts.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Oct 1;23(10):e29025. doi: 10.2196/29025. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 34519659 Free PMC article.
-
Mining of Opinions on COVID-19 Large-Scale Social Restrictions in Indonesia: Public Sentiment and Emotion Analysis on Online Media.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Aug 9;23(8):e28249. doi: 10.2196/28249. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 34280116 Free PMC article.
-
Media framing and expression of anti-China sentiment in COVID-19-related news discourse: An analysis using deep learning methods.Heliyon. 2022 Aug;8(8):e10419. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10419. Epub 2022 Aug 28. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36061028 Free PMC article.
-
News Sentiment Informed Time-series Analyzing AI (SITALA) to curb the spread of COVID-19 in Houston.Expert Syst Appl. 2021 Oct 15;180:115104. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115104. Epub 2021 Apr 29. Expert Syst Appl. 2021. PMID: 33942002 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Public Sentiments in Mainland China: Sentiment Analysis of Social Media Posts.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Aug 12;23(8):e29150. doi: 10.2196/29150. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 34280118 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acemoglu D., Naidu S., Restrepo P., Robinson J.A. Democracy does cause growth. J. Political Econ. 2019;127:47–100.
-
- Ahn Y., Kim D. Emotional trading in the cryptocurrency market. Financ. Res. Lett. 2020
-
- Alfaro, L., Chari, A., Greenland, A.N., Schott, P.K., 2020. Aggregate and firm-level stock returns during pandemics, in real time (No. w26950). National Bureau of Economic Research.
-
- Avi-Yonah, R.S., 2020. Taxes in the time of coronavirus: is it time to revive the excess profits tax? SSRN Electronic Journal.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
