Clinical study on sequential treatment of severe diarrhea irritable bowel syndrome with precision probiotic strains transplantation capsules, fecal microbiota transplantation capsules and live combined bacillus subtilis and enterococcus faecium capsules
- PMID: 36250045
- PMCID: PMC9555570
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1025889
Clinical study on sequential treatment of severe diarrhea irritable bowel syndrome with precision probiotic strains transplantation capsules, fecal microbiota transplantation capsules and live combined bacillus subtilis and enterococcus faecium capsules
Abstract
Objective: To study the effect of precision probiotic strains transplantation capsules on diarrhea irritable bowel syndrome compared with fecal microbiota transplantation capsules and live combined bacillus subtilis and enterococcus faecium capsules.
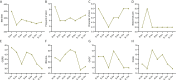
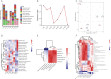
Methods: Two patients with severe irritable bowel syndrome were treated with precision probiotic strains transplantation capsules, fecal microbiota transplantation capsules and live combined bacillus subtilis and enterococcus faecium capsules in sequence. IBS-SSS, IBS-QoL, GSRS, stool frequency, stool character, degree of abdominal pain, GAD-7, and PHQ9 scores of patients at 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12 weeks of treatment were monitored and recorded, and stool samples were collected for metagenomics and metabolomics.
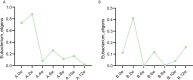
Results: It was found that the IBS-SSS score of patient case 1 decreased by 175 points and that of patient case 2 decreased by 100 points after treatment of precision probiotic strains transplantation capsules. There was no significant decrease after fecal microbiota transplantation capsules and live combined bacillus subtilis and enterococcus faecium capsules were used. At the same time, compared with fecal microbiota transplantation and live combined bacillus subtilis and enterococcus faecium capsules, the IBS QoL, stool frequency, stool character, degree of abdominal pain and GAD-7 score of patient case 1 improved more significantly by the precision probiotic strains transplantation capsules. And the stool frequency and stool character score of patient case 2 decreased more significantly. Intestinal microbiota also improved more significantly after the precise capsule transplantation treatment. And we found Eubacterium_ Eligens showed the same change trend in the treatment of two patients, which may play a role in the treatment.
Conclusion: precision probiotic strains transplantation capsules is more beneficial to improve the intestinal microbiota of patients than microbiota transplantation capsule and live combined bacillus subtilis and enterococcus faecium capsules, so as to better alleviate clinical symptoms. This study provides a more perfect and convenient therapeutic drugs for the treatment of IBS.
Keywords: Irritable bowel syndrome; fecal microbiota transplantation capsules; gut microbiota; live combined bacillus subtilis and enterococcus faecium capsules; precision transplantation.
Copyright © 2022 Lv, Ruan, Ping, Cheng, Tian, Xiao, Zhao, Chen and Wei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Baseline gut microbial profiles are associated with the efficacy of Bacillus subtilis and Enterococcus faecium in IBS-D.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2023 Apr;58(4):339-348. doi: 10.1080/00365521.2022.2136013. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 36281578
-
A randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of live Bifidobacterium longum CECT 7347 (ES1) and heat-treated Bifidobacterium longum CECT 7347 (HT-ES1) in participants with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome.Gut Microbes. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2338322. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2338322. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Gut Microbes. 2024. PMID: 38630015 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Fecal microbiota transplantation in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: an overview of current studies.J Appl Microbiol. 2023 Mar 1;134(3):lxad044. doi: 10.1093/jambio/lxad044. J Appl Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36882216 Review.
-
[The effects of probiotics on symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome].Korean J Gastroenterol. 2006 Jun;47(6):413-9. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16809947 Clinical Trial. Korean.
-
Fecal microbiota transplantation for irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Immunol. 2023 May 18;14:1136343. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1136343. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37275867 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Multifunctional Activity of a Postbiotic Preparation Derived from Lacticaseibacillus paracasei Postbiotic-P6.Foods. 2024 Jul 24;13(15):2326. doi: 10.3390/foods13152326. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39123515 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of calcium signaling and calcium deposition in microbial multicellularity.Trends Microbiol. 2023 Dec;31(12):1225-1237. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2023.06.005. Epub 2023 Jul 8. Trends Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37429751 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

