Aesthetic experience enhances first-person spatial representation
- PMID: 36251990
- PMCID: PMC9618070
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2201540119
Aesthetic experience enhances first-person spatial representation
Abstract
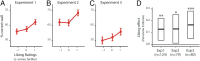
Episodic autobiographical memories are characterized by a spatial context and an affective component. But how do affective and spatial aspects interact? Does affect modulate the way we encode the spatial context of events? We investigated how one element of affect, namely aesthetic liking, modulates memory for location, in three online experiments (n = 124, 79, and 80). Participants visited a professionally curated virtual art exhibition. They then relocated previously viewed artworks on the museum map and reported how much they liked them. Across all experiments, liking an artwork was associated with increased ability to recall the wall on which it was hung. The effect was not explained by viewing time and appeared to modulate recognition speed. The liking-wall memory effect remained when participants attended to abstractness, rather than liking, and when testing occurred 24 h after the museum visit. Liking also modulated memory for the room where a work of art was hung, but this effect primarily involved reduced room memory for disliked artworks. Further, the liking-wall memory effect remained after controlling for effects of room memory. Recalling the wall requires recalling one's facing direction, so our findings suggest that positive aesthetic experiences enhance first-person spatial representations. More generally, a first-person component of positive affect transfers to wider spatial representation and facilitates the encoding of locations in a subject-centered reference frame. Affect and spatial representations are therefore important, and linked, elements of sentience and subjectivity. Memories of aesthetic experiences are also spatial memories of how we encountered a work of art. This linkage may have implications for museum design.
Keywords: aesthetics; affect; first person; memory; spatial representation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare a competing interest. The Museum of Contemporary Digital Art made available for sale a limited edition version of the exhibition poster as a non-fungible token (NFT).
Figures

References
-
- Postma A., Kessels R. P. C., van Asselen M., How the brain remembers and forgets where things are: The neurocognition of object-location memory. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 32, 1339–1345 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Leder H., Gerger G., Brieber D., “Aesthetic appreciation: Convergence from experimental aesthetics and physiology” in J.P. Huston and others (eds), Art, Aesthetics and the Brain, (Oxford 2015; online edn, Oxford Academic, 20 Aug 2015; ), pp. 57–78.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

