Monitoring the effect of TNF-alpha inhibitors on laboratory parameters and adverse effects in different diseases: a retrospective, single-center study
- PMID: 36252145
- PMCID: PMC9557780
- DOI: 10.5144/0256-4947.2022.309
Monitoring the effect of TNF-alpha inhibitors on laboratory parameters and adverse effects in different diseases: a retrospective, single-center study
Abstract
Background: The introduction of biological treatments has revolutionized the management of moderate-to-severe psoriasis. Multiple clinical trials have established the efficacy of biological agents in the treatment of moderate-to-severe psoriasis. Nevertheless, there are no clear indications for optimal monitoring intervals during treatment.
Objectives: Collect and analyze laboratory evaluation data from patients receiving biological therapy to provide a better understanding of the need for laboratory investigations before and during treatment with biological agents, and to analyze adverse events and other factors.
Design: Retrospective cohort SETTINGS: Tertiary care center in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Patients and methods: Data were collected from the electronic medical records of patients attending the dermatology, rheumatology, and gastroenterology clinics from June 2014 to June 2019. The laboratory parameters of patients who have received one of the TNF-alpha inhibitors (adalimumab, etanercept, or infliximab) were collected starting at baseline and up to at least one year from treatment initiation.
Main outcome measures: The time points at which patients developed significantly abnormal laboratory results during treatment with one of the TNF-alpha inhibitors.
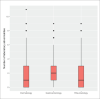
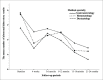
Sample size: 250 patients RESULTS: Most patients were treated with adalimumab (38.4%); a similar proportion (38%) with infliximab, whereas only 23.6% were treated with etanercept. The majority of the significant abnormal laboratory results occurred at baseline, 3-6 and 9-12 months. Most abnormalities were among patients using infliximab, followed by etanercept, and then adalimumab. The median number of laboratory abnormalities for dermatology patients was significantly lower than that for gastroenterology patients (P<.001), and for rheumatology patients (P=.002).
Conclusions: Because dermatology patients showed a lower median number of laboratory abnormalities than patients treated by other specialties in our study, we believe that dermatology patients require less frequent laboratory monitoring. Therefore, we recommend laboratory evaluation at baseline, after 3-6 months, 1 year from the beginning of treatment, and annually thereafter for patients using TNF-alpha inhibitor agents. However, more frequent testing might be warranted according to patient comorbidities, concomitant medications, and physician judgment.
Limitations: Single center and retrospective design.
Conflict of interest: None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Induction of Autoantibodies and Autoimmune Diseases in Patients with Psoriasis Receiving Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors.Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2017 Jun;108(5):445-456. doi: 10.1016/j.ad.2016.12.014. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2017. PMID: 28267955 English, Spanish.
-
Risk of herpes zoster in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-TNF-alpha agents.JAMA. 2009 Feb 18;301(7):737-44. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.146. JAMA. 2009. PMID: 19224750
-
Anti-TNF agents and nail psoriasis: a single-center, retrospective, comparative study.J Dermatolog Treat. 2013 Jun;24(3):162-8. doi: 10.3109/09546634.2011.646939. Epub 2012 Jan 4. J Dermatolog Treat. 2013. PMID: 22136334
-
Adverse reactions during biological drug therapy in psoriasis:clinical series and a review of the literature.G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2011 Aug;146(4):273-81. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2011. PMID: 21785393 Review.
-
Paradoxical Hidradenitis Suppurativa in Patients Receiving TNF-α Inhibitors: Case Series, Systematic Review, and Case Meta-Analysis.Dermatology. 2020;236(4):307-313. doi: 10.1159/000506074. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Dermatology. 2020. PMID: 32135533
Cited by
-
Prognostic factors for liver, blood and kidney adverse events from glucocorticoid sparing immune-suppressing drugs in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases: a prognostic systematic review.RMD Open. 2024 Jan 10;10(1):e003588. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2023-003588. RMD Open. 2024. PMID: 38199851 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors on lipid profiles in patients with psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 4;15:1354593. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1354593. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38500874 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Necrosis Alpha (TNF-α) Antagonists Used in Chronic Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases: Risks and their Minimization Measures.Curr Drug Saf. 2024;19(4):431-443. doi: 10.2174/0115748863274863231222023853. Curr Drug Saf. 2024. PMID: 38204274 Review.
-
Long-term mortality outcomes among immunotherapy recipients treated with dupilumab for the management of cutaneous immune-related adverse events.J Immunother Cancer. 2025 May 12;13(5):e010638. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-010638. J Immunother Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40355282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nestle FO, Kaplan DH, Barker J. Psoriasis. New England Journal of Medicine. 2009;361(5):496–509. - PubMed
-
- Yost J, Gudjonsson JE. The role of TNF inhibitors in psoriasis therapy: new implications for associated comorbidities. F1000 Med Rep. 2009. May 8;1:30. doi: 10.3410/M1-30. PMID: 20948750; PMCID: PMC2924720. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Smith CH, Anstey AV, Barker JN, Burden AD, Chalmers RJ, Chandler DA, Finlay AY, Griffiths CE, Jackson K, McHugh NJ, McKenna KE, Reynolds NJ, Ormerod AD; (Chair of Guideline Group) . British Association of Dermatologists’ guidelines for biologic interventions for psoriasis 2009. Br J Dermatol. 2009. Nov;161(5):987–1019. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2009.09505.x. PMID: 19857207. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Emer JJ, Frankel A, Zeichner JA. A practical approach to monitoring patients on biological agents for the treatment of psoriasis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2010. Aug;3(8):20–6. PMID: 20877538; PMCID: PMC2945861. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials