Efficacy and safety of pre-gastroscopy commercial carbohydrate-rich whey protein beverage vs. plain water: a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 36253448
- PMCID: PMC9576750
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-22363-1
Efficacy and safety of pre-gastroscopy commercial carbohydrate-rich whey protein beverage vs. plain water: a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
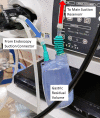
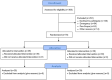
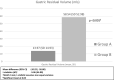
Clinical benefits and safety of carbohydrate loading pre-gastroscopy remain unclear. We aimed to determine the effects of a commercial carbohydrate-rich whey protein beverage versus plain water given pre-gastroscopy on gastric residual volume and well-being, and to determine adverse events. This was a single centre, single-blinded, parallel-group, sex-stratified randomized controlled trial. Participants were randomized either to carbohydrate-rich whey protein beverage group (Resource®, Nestle Health Science) or control group (250 ml plain water) given pre-gastroscopy. Gastric contents were aspirated into a suction reservoir bottle to determine the gastric residual volume (GRV). Visual analogue scale (VAS) of well-being (anxiety, hunger, thirst, tiredness, and weakness) was compared before and after the intervention. Adverse events were also evaluated post-intervention. Of 369 screened, 78 participants (36 males, mean age 49 ± 14.3 years) were randomized. Compared with the control group, carbohydrate beverage was associated with significantly higher GRV (p < 0.001). Anxiety was less after intervention with carbohydrate beverage (p = 0.016), and after adjustment for confounders, fewer participants also experienced hunger (p = 0.043) and thirst (p = 0.021). No serious adverse events were reported with both interventions. Commercial carbohydrate-rich whey protein beverage is associated with higher gastric residual volume, better well-being and safe.Trial registration Clinicaltrial.gov. Identifier: NCT03948594, Date of registration: 14/05/2019.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of pre-endoscopy maltodextrin beverage on gastric residual volume and patient's well-being: a randomised controlled trial.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 16;13(1):20078. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-47357-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37973795 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of a carbohydrate-rich beverage on rate of cesarean delivery in primigravidae with epidural labor analgesia: a multicenter randomized trial.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2022 Apr 19;22(1):339. doi: 10.1186/s12884-022-04659-2. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2022. PMID: 35440017 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safe intake of an oral supplement containing carbohydrates and whey protein shortly before sedation to gastroscopy; a double blind, randomized trial.Nutr Hosp. 2014 Mar 1;29(3):681-6. doi: 10.3305/nh.2014.29.3.7161. Nutr Hosp. 2014. PMID: 24559015 Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of consuming carbohydrate-electrolyte beverages on gastric emptying and fluid absorption during and following exercise.Sports Med. 1987 Sep-Oct;4(5):322-51. doi: 10.2165/00007256-198704050-00002. Sports Med. 1987. PMID: 3313617 Review.
-
Nothing by mouth at midnight: saving or starving? A literature review.Gastroenterol Nurs. 2014 Jan-Feb;37(1):14-23. doi: 10.1097/SGA.0000000000000018. Gastroenterol Nurs. 2014. PMID: 24476828 Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of pre-endoscopy maltodextrin beverage on gastric residual volume and patient's well-being: a randomised controlled trial.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 16;13(1):20078. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-47357-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37973795 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Carmichael JC, Keller DS, Baldini G, Bordeianou L, Weiss E, Lee L, et al. Clinical practice guideline for enhanced recovery after colon and rectal surgery from the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons (ASCRS) and Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) Surg. Endosc. 2017;31:3412–3436. doi: 10.1007/s00464-017-5722-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical