Structural basis of colibactin activation by the ClbP peptidase
- PMID: 36253550
- PMCID: PMC9889268
- DOI: 10.1038/s41589-022-01142-z
Structural basis of colibactin activation by the ClbP peptidase
Abstract
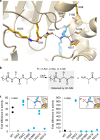
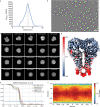
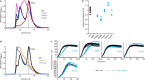
Colibactin, a DNA cross-linking agent produced by gut bacteria, is implicated in colorectal cancer. Its biosynthesis uses a prodrug resistance mechanism: a non-toxic precursor assembled in the cytoplasm is activated after export to the periplasm. This activation is mediated by ClbP, an inner-membrane peptidase with an N-terminal periplasmic catalytic domain and a C-terminal three-helix transmembrane domain. Although the transmembrane domain is required for colibactin activation, its role in catalysis is unclear. Our structure of full-length ClbP bound to a product analog reveals an interdomain interface important for substrate binding and enzyme stability and interactions that explain the selectivity of ClbP for the N-acyl-D-asparagine prodrug motif. Based on structural and biochemical evidence, we propose that ClbP dimerizes to form an extended substrate-binding site that can accommodate a pseudodimeric precolibactin with its two terminal prodrug motifs in the two ClbP active sites, thus enabling the coordinated activation of both electrophilic warheads.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
E.P.B. and M.R.V. are listed as inventors on a provisional patent (US application 63/135,825) which relates to the methods and ClbP inhibitors described in Reference 22. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


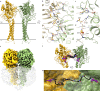







References
-
- Nougayrede JP, et al. Escherichia coli induces DNA double-strand breaks in eukaryotic cells. Science. 2006;313:848–851. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

