Neuromuscular diseases and social distance resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 36254444
- PMCID: PMC9685824
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0042-1755232
Neuromuscular diseases and social distance resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus 2 severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV-2), generically called COVID-2019, classified as a pandemic by the World Health Organization, has made health practices around the world face unique challenges. Since then, physical distancing and measures such as confinement have been adopted by different governments to control human-to-human transmission. This distance affected the treatment of individuals with progressive diseases such as neuromuscular diseases (NMDs).
Objective: To identify how patients with NMDs performed the therapeutic routine during social distancing and confinement resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods: Application of a questionnaire prepared in the Google forms application, whose link for access and participation was sent by email or WhatssApp for family members and/or individuals with DNMs to respond. The questionnaire consisted of multiple-choice questions, divided into the following sections: personal data, treatments performed before and during the pandemic, activities performed during confinement, and characterization of motor function in activities of daily living comprising the period between September and October 2020.
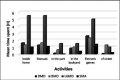
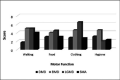
Results: We observed a significant reduction in medical appointments for patients with NMDs. On the other hand, the results showed that most patients underwent motor and/or respiratory physiotherapy in person or by telemonitoring. The study participants reported spending more time playing indoors, and all pointed out motor changes during social distancing.
Conclusion: There were changes in the therapeutic routine of patients with NMDs during the period of social distancing due to COVID-19.
Antecedentes: A síndrome respiratória aguda grave por coronavírus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), genericamente chamada de COVID-2019, classificada como pandemia pela Organização Mundial da Saúde, tem feito as práticas de saúde em todo o mundo enfrentar desafios únicos. Desde então, o distanciamento físico e medidas como o confinamento foram adotadas por diferentes governos para controlar a transmissão inter-humana. Este distanciamento afetou o tratamento de indivíduos com doenças progressivas, como no caso das doenças neuromusculares (DNMs).
Objetivo: Identificar como os pacientes com DNMs realizaram a rotina terapêutica durante o distanciamento social e confinamento decorrentes da pandemia de COVID-19. MéTODOS: Aplicação de um questionário elaborado no aplicativo Google forms, cujo link para acesso e participação foi enviado por e-mail ou WhatssApp para familiares e/ou indivíduos com DNMs responderem. O questionário consistiu em questões de múltipla escolha, dividido nas seguintes sessões: dados pessoais, tratamentos realizados antes e durante a pandemia, atividades realizadas durante o confinamento e caracterização das funções motoras nas atividades de vida diária, referente ao período de setembro a outubro de 2020.
Resultados: Observamos uma redução significativa nas consultas médicas dos pacientes com DNMs. Por outro lado, os resultados demonstraram que a maior parte dos pacientes realizou fisioterapia motora e/ou respiratória de modo presencial ou por telemonitoramento. Os participantes do estudo relataram gastar mais tempo com atividades dentro de casa, além de todos terem apontado mudanças motoras durante o distanciamento social. CONCLUSãO: Houve mudanças na rotina terapêutica de pacientes com DNM durante o período de distanciamento social da COVID-19.
Academia Brasileira de Neurologia. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commecial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Yang ML, Finkel RS. Overview of paediatric neuromuscular disorders and related pulmonary issues: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2010;11(01):9–17. - PubMed
-
- WMS . Covid-19 e doentes com doenças neuromusculares: Posição e recomendações da “World Muscle Society” (WMS) Versão 2 – atualização em 06/04/2020. Brazil: https://www.worldmusclesociety.org/files/COVID19/2020-04-02/2020-04-02-W... (Brazilian)
-
- Brasil. Ministério da saúde https://antigo.saude.gov.br/saude-de-a-z/doencas-raras .
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous