Deep, deep learning with BART
- PMID: 36254526
- PMCID: PMC10898647
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.29485
Deep, deep learning with BART
Abstract
Purpose: To develop a deep-learning-based image reconstruction framework for reproducible research in MRI.
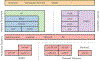
Methods: The BART toolbox offers a rich set of implementations of calibration and reconstruction algorithms for parallel imaging and compressed sensing. In this work, BART was extended by a nonlinear operator framework that provides automatic differentiation to allow computation of gradients. Existing MRI-specific operators of BART, such as the nonuniform fast Fourier transform, are directly integrated into this framework and are complemented by common building blocks used in neural networks. To evaluate the use of the framework for advanced deep-learning-based reconstruction, two state-of-the-art unrolled reconstruction networks, namely the Variational Network and MoDL, were implemented.
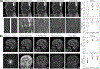
Results: State-of-the-art deep image-reconstruction networks can be constructed and trained using BART's gradient-based optimization algorithms. The BART implementation achieves a similar performance in terms of training time and reconstruction quality compared to the original implementations based on TensorFlow.
Conclusion: By integrating nonlinear operators and neural networks into BART, we provide a general framework for deep-learning-based reconstruction in MRI.
Keywords: MRI; automatic differentiation; deep learning; image reconstruction; inverse problems; parallel imaging.
© 2022 The Authors. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Sodickson DK, Manning WJ Simultaneous acquisition of spatial harmonics (SMASH): fast imaging with radiofrequency coil arrays. Magn. Reson. Med. 1997;38(4):591–603. - PubMed
-
- Griswold MA, Jakob PM, Heidemann RM, et al. Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magn. Reson. Med. 2002;47(6):1202–1210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

