Antenatal corticosteroids in Singapore: a clinical and scientific assessment
- PMID: 36254928
- PMCID: PMC11479002
- DOI: 10.4103/SINGAPOREMEDJ.SMJ-2022-014
Antenatal corticosteroids in Singapore: a clinical and scientific assessment
Abstract
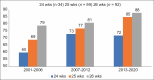
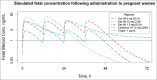
Preterm birth (PTB; delivery prior to 37 weeks' gestation) is the leading cause of early childhood death in Singapore today. Approximately 9% of Singaporean babies are born preterm; the PTB rate is likely to increase given the increased use of assisted reproduction technologies, changes in the incidence of gestational diabetes/high body mass index and the ageing maternal population. Antenatal administration of dexamethasone phosphate is a key component of the obstetric management of Singaporean women who are at risk of imminent preterm labour. Dexamethasone improves preterm outcomes by crossing the placenta to functionally mature the fetal lung. The dexamethasone regimen used in Singapore today affords a very high maternofetal drug exposure over a brief period of time. Drawing on clinical and experimental data, we reviewed the pharmacokinetic profile and pharmacodynamic effects of dexamethasone treatment regimen in Singapore, with a view to creating a development pipeline for optimising this critically important antenatal therapy.
Copyright © 2024 Copyright: © 2024 Singapore Medical Journal.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Department of Statistics Ministry of Trade & Industry Republic of Singapore. Trends in Infant Mortality Rate and Related Indicators. 2019. [[Last accessed on 2022 Jan 17]]. Available from: https://www.singstat.gov.sg/-/media/files/publications/population/ssn119... .
-
- Ministry of Health Republic of Singapore. Management of Preterm Labour. Singapore: 2001.
-
- Jobe AH, Goldenberg RL. Antenatal corticosteroids: An assessment of anticipated benefits and potential risks. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;219:62–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

