Integrin binding peptides facilitate growth and interconnected vascular-like network formation of rat primary cortical vascular endothelial cells in vitro
- PMID: 36254992
- PMCID: PMC9827785
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.355760
Integrin binding peptides facilitate growth and interconnected vascular-like network formation of rat primary cortical vascular endothelial cells in vitro
Abstract
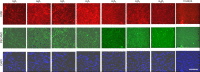
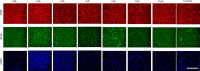
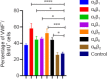
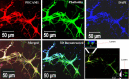
Neovascularization and angiogenesis in the brain are important physiological processes for normal brain development and repair/regeneration following insults. Integrins are cell surface adhesion receptors mediating important function of cells such as survival, growth and development during tissue organization, differentiation and organogenesis. In this study, we used an integrin-binding array platform to identify the important types of integrins and their binding peptides that facilitate adhesion, growth, development, and vascular-like network formation of rat primary brain microvascular endothelial cells. Brain microvascular endothelial cells were isolated from rat brain on post-natal day 7. Cells were cultured in a custom-designed integrin array system containing short synthetic peptides binding to 16 types of integrins commonly expressed on cells in vertebrates. After 7 days of culture, the brain microvascular endothelial cells were processed for immunostaining with markers for endothelial cells including von Willibrand factor and platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule. 5-Bromo-2'-dexoyuridine was added to the culture at 48 hours prior to fixation to assess cell proliferation. Among 16 integrins tested, we found that α5β1, αvβ5 and αvβ8 greatly promoted proliferation of endothelial cells in culture. To investigate the effect of integrin-binding peptides in promoting neovascularization and angiogenesis, the binding peptides to the above three types of integrins were immobilized to our custom-designed hydrogel in three-dimensional (3D) culture of brain microvascular endothelial cells with the addition of vascular endothelial growth factor. Following a 7-day 3D culture, the culture was fixed and processed for double labeling of phalloidin with von Willibrand factor or platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule and assessed under confocal microscopy. In the 3D culture in hydrogels conjugated with the integrin-binding peptide, brain microvascular endothelial cells formed interconnected vascular-like network with clearly discernable lumens, which is reminiscent of brain microvascular network in vivo. With the novel integrin-binding array system, we identified the specific types of integrins on brain microvascular endothelial cells that mediate cell adhesion and growth followed by functionalizing a 3D hydrogel culture system using the binding peptides that specifically bind to the identified integrins, leading to robust growth and lumenized microvascular-like network formation of brain microvascular endothelial cells in 3D culture. This technology can be used for in vitro and in vivo vascularization of transplants or brain lesions to promote brain tissue regeneration following neurological insults.
Keywords: 3D culture; angiogenesis; brain microvascular endothelial cells; hydrogel; integrins; platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule (PECAM-1); vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF); vascularization.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
Similar articles
-
An integrin-binding array platform identifies αvβ8 and α5β1 integrins on rat primary cortical neurons to support their survival and growth.J Neurosci Methods. 2020 Jun 1;339:108729. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2020.108729. Epub 2020 Apr 17. J Neurosci Methods. 2020. PMID: 32305448 Free PMC article.
-
Functional overlap and cooperativity among alphav and beta1 integrin subfamilies during skin angiogenesis.J Invest Dermatol. 2003 Jun;120(6):1100-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12236.x. J Invest Dermatol. 2003. PMID: 12787141
-
[Preliminary study on the effect of vascular endothelial growth factor-loaded self-assembled peptide hydrogel on angiogenesis and vascularization of human umbilical vein endothelial cells].Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Oct 9;55(10):757-764. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112144-20200331-00182. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33045788 Chinese.
-
Cell adhesion and regulatory molecules involved in tumor formation, hemostasis, and wound healing.Head Neck. 1995 Mar-Apr;17(2):140-7. doi: 10.1002/hed.2880170212. Head Neck. 1995. PMID: 7558812 Review.
-
New artery of knowledge: 3D models of angiogenesis.Vasc Biol. 2019 Dec 3;1(1):H135-H143. doi: 10.1530/VB-19-0026. eCollection 2019. Vasc Biol. 2019. PMID: 32923965 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from rat fibroblasts and optimization of its differentiation into mature functional neurons.J Neurosci Methods. 2024 Jun;406:110114. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2024.110114. Epub 2024 Mar 24. J Neurosci Methods. 2024. PMID: 38522633 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advancement in vascularized tissue-engineered bone based on materials design and modification.Mater Today Bio. 2023 Nov 11;23:100858. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100858. eCollection 2023 Dec. Mater Today Bio. 2023. PMID: 38024843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RhoJ: an emerging biomarker and target in cancer research and treatment.Cancer Gene Ther. 2024 Oct;31(10):1454-1464. doi: 10.1038/s41417-024-00792-6. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Cancer Gene Ther. 2024. PMID: 38858534 Review.
References
-
- Brooks PC, Clark RA, Cheresh DA. Requirement of vascular integrin alpha v beta 3 for angiogenesis. Science. 1994;264:569–571. - PubMed
-
- Demircioglu F, Hodivala-Dilke K. αvβ3 Integrin and tumour blood vessels-learning from the past to shape the future. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2016;42:121–127. - PubMed
-
- Dudvarski StankovićN, Bicker F, Keller S, Jones DT, Harter PN, Kienzle A, Gillmann C, Arnold P, Golebiewska A, Keunen O, Giese A, von Deimling A, Bäuerle T, Niclou SP, Mittelbronn M, Ye W, Pfister SM, Schmidt MHH. EGFL7 enhances surface expression of integrin α5β1 to promote angiogenesis in malignant brain tumors. EMBO Mol Med. 2018;10:e8420. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

