An introduction to photon-counting detector CT (PCD CT) for radiologists
- PMID: 36255601
- PMCID: PMC9974724
- DOI: 10.1007/s11604-022-01350-6
An introduction to photon-counting detector CT (PCD CT) for radiologists
Abstract
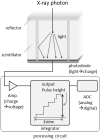
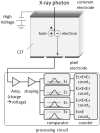
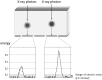
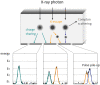
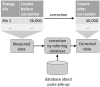
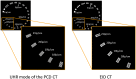
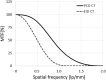
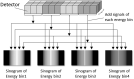
The basic performance of photon-counting detector computed tomography (PCD CT) is superior to conventional CT (energy-integrating detector CT: EID CT) because its spatial- and contrast resolution of soft tissues is higher, and artifacts are reduced. Because the X-ray photon energy separation is better with PCD CT than conventional EID-based dual-energy CT, it has the potential to improve virtual monochromatic- and virtual non-contrast images, material decomposition including quantification of the iodine distribution, and K-edge imaging. Therefore, its clinical applicability may be increased. Although the image quality of PCD CT scans is superior to that of EID CT currently, further improvement may be possible. The introduction of iterative image reconstruction and reconstruction with deep convolutional neural networks will be useful.
Keywords: Energy separation; Energy-integrating detector CT; K-edge imaging; Photon-counting detector CT; Spatial resolution.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Kazuo Awai received a research grant from Canon Medical Systems Co. Ltd. and FUJIFILM Healthcare Corporation. Isao Takahashi is an employee of FUJIFILM Healthcare Corporation and FUJIFILM Corporation. The other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

