Lysosomal positioning regulates Rab10 phosphorylation at LRRK2+ lysosomes
- PMID: 36256825
- PMCID: PMC9618077
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2205492119
Lysosomal positioning regulates Rab10 phosphorylation at LRRK2+ lysosomes
Abstract
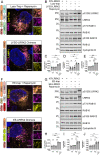
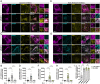
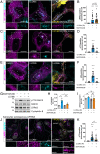
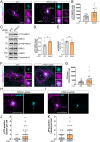
Genetic variation at the leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) locus contributes to an enhanced risk of familial and sporadic Parkinson's disease. Previous data have demonstrated that recruitment to various membranes of the endolysosomal system results in LRRK2 activation. However, the mechanism(s) underlying LRRK2 activation at endolysosomal membranes and the cellular consequences of these events are still poorly understood. Here, we directed LRRK2 to lysosomes and early endosomes, triggering both LRRK2 autophosphorylation and phosphorylation of the direct LRRK2 substrates Rab10 and Rab12. However, when directed to the lysosomal membrane, pRab10 was restricted to perinuclear lysosomes, whereas pRab12 was visualized on both peripheral and perinuclear LRRK2+ lysosomes, suggesting that lysosomal positioning provides additional regulation of LRRK2-dependent Rab phosphorylation. Anterograde transport of lysosomes to the cell periphery by increasing the expression of ARL8B and SKIP or by knockdown of JIP4 blocked the recruitment and phosphorylation of Rab10 by LRRK2. The absence of pRab10 from the lysosomal membrane prevented the formation of a lysosomal tubulation and sorting process we previously named LYTL. Conversely, overexpression of RILP resulted in lysosomal clustering within the perinuclear area and increased LRRK2-dependent Rab10 recruitment and phosphorylation. The regulation of Rab10 phosphorylation in the perinuclear area depends on counteracting phosphatases, as the knockdown of phosphatase PPM1H significantly increased pRab10 signal and lysosomal tubulation in the perinuclear region. Our findings suggest that LRRK2 can be activated at multiple cellular membranes, including lysosomes, and that lysosomal positioning further provides the regulation of some Rab substrates likely via differential phosphatase activity or effector protein presence in nearby cellular compartments.
Keywords: JIP4; LLOMe; LYTL; Parkinson's disease; kinase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures




References
-
- Paisán-Ruíz C., et al. , Cloning of the gene containing mutations that cause PARK8-linked Parkinson’s disease. Neuron 44, 595–600 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Nalls M. A., et al. ; 23andMe Research Team; System Genomics of Parkinson’s Disease Consortium; International Parkinson’s Disease Genomics Consortium, Identification of novel risk loci, causal insights, and heritable risk for Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Lancet Neurol. 18, 1091–1102 (2019). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Greggio E., et al. , Kinase activity is required for the toxic effects of mutant LRRK2/dardarin. Neurobiol. Dis. 23, 329–341 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

