Real-world experience among patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma after Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor failure in Europe: The SCHOLAR-2 retrospective chart review study
- PMID: 36257914
- PMCID: PMC10812379
- DOI: 10.1111/bjh.18519
Real-world experience among patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma after Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor failure in Europe: The SCHOLAR-2 retrospective chart review study
Abstract
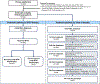
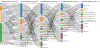
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) after relapse is associated with poor prognosis. No standard of care exists and available evidence for treatments is limited, particularly in patients who fail Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTKi) therapy. This multicentre retrospective chart review study, SCHOLAR-2, addresses this knowledge gap and reports on data collected from 240 patients with relapsed/refractory MCL in Europe who were treated with BTKi-based therapy between July 2012 and July 2018, and had experienced disease progression while on BTKi therapy or discontinued BTKi therapy due to intolerance. The median overall survival (OS) from initiation of first BTKi therapy was 14.6 months (95% confidence interval [CI] 11.6-20.0) in the overall cohort, 5.5 months (95% CI 3.9-8.2) in 91 patients without post-BTKi therapy, and 23.8 months (95% CI 18.9-30.1) in 149 patients who received post-BTKi therapy (excluding chimeric antigen receptor T-cell treatment). In the latter group, patients received a median of one (range, one to seven) line of post-BTKi therapy, with lenalidomide-containing regimens and bendamustine plus rituximab being the most frequently administered; the median OS from initiation of first post-BTKi therapy was 9.7 months (95% CI 6.3-12.7). These results provide a benchmark for survival in patients with R/R MCL receiving salvage therapy after BTKi failure.
Keywords: Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor; mantle cell lymphoma; post-BTKi; real-world evidence; survival.
© 2022 The Authors. British Journal of Haematology published by British Society for Haematology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
GH has received research support for the submitted work from Kite, a Gilead Company; has received grants or contracts from Celgene, Kite, a Gilead Company, Incyte, Janssen, Morphosys, Pfizer, and Roche; has received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Abbvie, ADC, AstraZeneca, Genmab, Kite, a Gilead Company, Incyte, Janssen, Morphosys, Novartis, Roche, and Takeda; has received support for attending meetings and/or travel from Kite, a Gilead Company, and Janssen; and has participated in on a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board for Miltenyie. LO has received support for attending meetings and/or travel from Roche and AstraZeneca; and has participated on a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board for Roche and Gilead Sciences. PLZ has received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Roche, Takeda, Gilead Sciences, Sanofi, Incyte, Novartis, Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS), AstraZeneca, and Kyowa Kirin. KL has received consulting fees from Genmab, Roche, Kite, a Gilead Company, and Beigene; has received payment or honoraria for educational events from Abbvie and Celgene/BMS; has received support for attending meetings from BMS and Takeda; and has leadership or fiduciary role in NCRI, EHA LyG, WiL, and Epcoritamab Global Council. MJ has received grants or contracts from Roche, Abbvie, and BMS; has received consulting fees from Gilead Sciences, Janssen, and Abbvie; has received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Janssen; has participated on Data Safety Monitoring board or Advisory Board for GenMab. SS has received grants or contracts; consulting fees; payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events; support for attending meetings and/or travel; equipment, materials, drugs, medical, writing, gifts or other services; and payments for participation on a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board from AbbVie, Acerta, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, BMS, Celgene, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, GSK, Hoffmann-La Roche, Incyte, Infinity, Janssen, Novartis, Pharmacyclics, Sunesis, and Verastem. JL has received payment or honoraria for educational events and support for attending meetings from Kite, a Gilead Company. VRZ has received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or education events from Janssen; has received support for attending meetings and/or travel from Janssen; and has participated on Data Safety Monitoring board or Advisory Board for Gilead Sciences and Novartis. JMS has received honoraria for educational events from Roche, Kite, a Gilead Company, Celgene/BMS, Novartis, Janssen, Takeda, and Incyte; has received support for attending meetings and/or travel from Roche; and has received honoraria for participation in Advisory Board from Roche, Kite, a Gilead Company, Celgene/BMS, Novartis, Janssen, Incyte, Beigene, Lilly. TAE has received payments or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Loxo Oncology, Eli Lilly, Beigene, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Incyte, Abbvie, Roche, and Kite, a Gilead Company; has received grants or contracts from AstraZeneca and Beigene; has received consulting fees from Loxo Oncology, Eli Lilly, Beigene, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Incyte, Secura Bio, Abbvie, Roche, and Kite a Gilead Company; and has received payments for travel to scientific congress from Abbvie. JJW is an employee of Kite, a Gilead Company; has received honoraria from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI), both as a member of the Rare Disease Advisory Panel, and as a grants reviewer for the Improving Methods Program; has received travel/meeting support from Kite, a Gilead Company, and Amgen; owns stock in Gilead Sciences, Amgen, Abbott, AbbVie, Pfizer, Roche, Curis, Avid Biosciences, Evofem, Lensar, VBI Vaccines, and Viracta Therapeutics. RS is an employee of Kite, a Gilead Company, and was previously employed by Amgen; has led advisory boarding meeting for Kite, a Gilead Company; and owns stocks in Gilead Sciences and Amgen. SW has received writing support for the submitted work from Kite, a Gilead Company; has received consulting fees from Kite, a Gilead Company, Allergan, Amgen, and Johnson & Johnson; and has received support for attending meetings from Kite, a Gilead Company. GS has received consulting fees from Abbvie, Celgene/BMS, Epizyme, Genmab, Incyte, Janssen, Kite, a Gilead Company, Loxo, Milteniy, Molecular Partners, Morphosys, Nordic Nanovector, Novartis, Rapt, and Takeda; has received payment or honoraria for speaking in symposium from Bayer, Epizyme, and Regeneron; has participated on a Data Safety Monitoring board or Advisory Board for Beigene; and has stock or stock options from Owkin. JMHC, SK, and JEP are employees of PRECISIONheor which received funding for this study from Kite, a Gilead Company. MD, EG, AV, AO, CT, AJU, LF, and JR declare no competing interests.
Figures
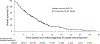
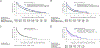
References
-
- McKay P, Leach M, Jackson B, Robinson S, Rule S. Guideline for the management of mantle cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol 2018;182(1):46–62. - PubMed
-
- Dreyling M, Campo E, Hermine O, Jerkeman M, Le Gouill S, Rule S, et al. Newly diagnosed and relapsed mantle cell lymphoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 2017;28(suppl_4):iv62–iv71. - PubMed
-
- Avivi I, Goy A. Refining the mantle cell lymphoma paradigm: Impact of novel therapies on current practice. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2015;21(17):3853–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

