Role of C-terminal domain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis PE6 (Rv0335c) protein in host mitochondrial stress and macrophage apoptosis
- PMID: 36258102
- PMCID: PMC9579591
- DOI: 10.1007/s10495-022-01778-1
Role of C-terminal domain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis PE6 (Rv0335c) protein in host mitochondrial stress and macrophage apoptosis
Abstract
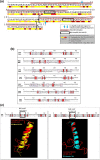
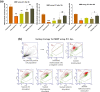
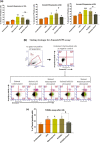
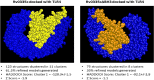
PE/PPE proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) target the host organelles to dictate the outcome of infection. This study investigated the significance of PE6/Rv0335c protein's unique C-terminal in causing host mitochondrial perturbations and apoptosis. In-silico analysis revealed that similar to eukaryotic apoptotic Bcl2 proteins, Rv0335c had disordered, hydrophobic C-terminal and two BH3-like motifs in which one was located at C-terminal. Also, Rv0335c's N terminal had mitochondrial targeting sequence. Since, C-terminal of Bcl2 proteins are crucial for mitochondria targeting and apoptosis; it became relevant to evaluate the role of Rv0335c's C-terminal domain in modulating host mitochondrial functions and apoptosis. To confirm this, in-vitro experiments were conducted with Rv0335c whole protein and Rv0335c∆Cterm (C-terminal domain deleted Rv0335c) protein. Rv0335c∆Cterm caused significant reduction in mitochondrial perturbations and Caspase-mediated apoptosis of THP1 macrophages in comparison to Rv0335c. However, the deletion of C-terminal domain didn't affect Rv0335c's ability to localize to mitochondria. Nine Ca2+ binding residues were predicted within Rv0335c and four of them were at the C-terminal. In-vitro studies confirmed that Rv0335c caused significant increase in intracellular calcium influx whereas Rv0335c∆Cterm had insignificant effect on Ca2+ influx. Rv0335c has been reported to be a TLR4 agonist and, we observed a significant reduction in the expression of TLR4-HLA-DR-TNF-α in response to Rv0335c∆Cterm protein also suggesting the role of Rv0335c's C-terminal domain in host-pathogen interaction. These findings indicate the possibility of Rv0335c as a molecular mimic of eukaryotic Bcl2 proteins which equips it to cause host mitochondrial perturbations and apoptosis that may facilitate pathogen persistence.
Keywords: BH3-like motif; Mitochondria-mediated intrinsic apoptosis; Mycobacterium tuberculosis; Rv0335c; Unique C-terminal domain.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures














Similar articles
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Protein PE6 (Rv0335c), a Novel TLR4 Agonist, Evokes an Inflammatory Response and Modulates the Cell Death Pathways in Macrophages to Enhance Intracellular Survival.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 12;12:696491. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.696491. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34322125 Free PMC article.
-
C-terminal region of Rv1039c (PPE15) protein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis targets host mitochondria to induce macrophage apoptosis.Apoptosis. 2024 Oct;29(9-10):1757-1779. doi: 10.1007/s10495-024-01965-2. Epub 2024 Apr 14. Apoptosis. 2024. PMID: 38615303
-
The PGRS Domain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis PE_PGRS Protein Rv0297 Is Involved in Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Apoptosis through Toll-Like Receptor 4.mBio. 2018 Jun 19;9(3):e01017-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01017-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 29921671 Free PMC article.
-
Role of PE/PPE proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in triad of host mitochondria, oxidative stress and cell death.Microb Pathog. 2024 Aug;193:106757. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106757. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Microb Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38908454 Review.
-
Functional Implications of the spectrum of BCL2 mutations in Lymphoma.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2016 Jul-Sep;769:1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2016.06.001. Epub 2016 Jun 16. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2016. PMID: 27543313 Review.
Cited by
-
Recognition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by macrophage Toll-like receptor and its role in autophagy.Inflamm Res. 2024 May;73(5):753-770. doi: 10.1007/s00011-024-01864-x. Epub 2024 Apr 2. Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38563966 Review.
-
Exploring host-pathogen interactions in the Dictyostelium discoideum-Mycobacterium marinum infection model of tuberculosis.Dis Model Mech. 2024 Jul 1;17(7):dmm050698. doi: 10.1242/dmm.050698. Epub 2024 Jul 22. Dis Model Mech. 2024. PMID: 39037280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The MICOS Complex Subunit Mic60 is Hijacked by Intracellular Bacteria to Manipulate Mitochondrial Dynamics and Promote Bacterial Pathogenicity.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Dec;11(46):e2406760. doi: 10.1002/advs.202406760. Epub 2024 Oct 21. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39431455 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological effects of the PE/PPE family proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and related vaccines.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 27;14:1255920. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1255920. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37841250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A potent subset of Mycobacterium tuberculosis glycoproteins as relevant candidates for vaccine and therapeutic target.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 14;13(1):22194. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49665-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38092899 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO . WHO global TB report. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

