NUPR1 contributes to radiation resistance by maintaining ROS homeostasis via AhR/CYP signal axis in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 36258210
- PMCID: PMC9580158
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-022-02554-3
NUPR1 contributes to radiation resistance by maintaining ROS homeostasis via AhR/CYP signal axis in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Radiotherapy (RT) is one of the major therapeutic approaches to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Ionizing radiation (IR) inducing the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) leads to a promising antitumor effect. However, the dysregulation of the redox system often causes radioresistance and impairs the efficacy of RT. Increasing evidence indicates that nuclear protein 1 (NUPR1) plays a critical role in redox reactions. In this study, we aim to explore the role of NUPR1 in maintaining ROS homeostasis and radioresistance in HCC.
Methods: The radioresistant role of NUPR1 was determined by colony formation assay, comet assay in vitro, and xenograft tumor models in vivo. Probes for ROS, apoptosis assay, and lipid peroxidation assay were used to investigate the functional effect of NUPR1 on ROS homeostasis and oxidative stress. RNA sequencing and co-immunoprecipitation assay were performed to clarify the mechanism of NUPR1 inhibiting the AhR/CYP signal axis. Finally, we analyzed clinical specimens to assess the predictive value of NUPR1 and AhR in the radiotherapeutic efficacy of HCC.
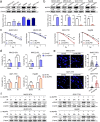
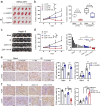
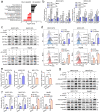
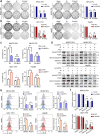
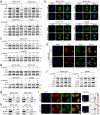
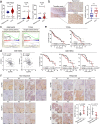
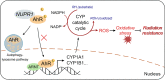
Results: We demonstrated that NUPR1 was upregulated in HCC tissues and verified that NUPR1 increased the radioresistance of HCC in vitro and in vivo. NUPR1 alleviated the generation of ROS and suppressed oxidative stress, including apoptosis and lipid peroxidation by downregulating cytochrome P450 (CYP) upon IR. ROS scavenger N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) and CYP inhibitor alizarin restored the viability of NUPR1-knockdown cells during IR. Mechanistically, the interaction between NUPR1 and aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) promoted the degradation and decreased nuclear translation of AhR via the autophagy-lysosome pathway, followed by being incapable of CYP's transcription. Furthermore, genetically and pharmacologically activating AhR abrogated the radioresistant role of NUPR1. Clinical data suggested that NUPR1 and AhR could serve as novel biomarkers for predicting the radiation response of HCC.
Conclusions: Our findings revealed the role of NUPR1 in regulating ROS homeostasis and oxidative stress via the AhR/CYP signal axis upon IR. Strategies targeting the NUPR1/AhR/CYP pathway may have important clinical applications for improving the radiotherapeutic efficacy of HCC.
Keywords: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor; Hepatocellular carcinoma; NUPR1; Oxidative stress; Radioresistance; Reactive oxygen species.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
UBE2T-regulated H2AX monoubiquitination induces hepatocellular carcinoma radioresistance by facilitating CHK1 activation.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Oct 21;39(1):222. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01734-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33087136 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of AhR/CYP1s signaling pathway mediated ROS production in uremic cardiomyopathy.Toxicol Lett. 2024 May 15;396:81-93. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2024.04.005. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Toxicol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38670245
-
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand ITE inhibits cell proliferation and migration and enhances sensitivity to drug-resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cell Physiol. 2021 Jan;236(1):178-192. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29832. Epub 2020 Jun 8. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 32510618
-
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Oxidative Stress as a Double Agent and Its Biological and Therapeutic Significance.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 16;23(12):6719. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126719. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The involvement of ROS-regulated programmed cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2024 May;197:104361. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2024.104361. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38626849 Review.
Cited by
-
Suppression of NUPR1 in fibroblast-like synoviocytes reduces synovial fibrosis via the Smad3 pathway.J Transl Med. 2024 Aug 1;22(1):715. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05540-w. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39090667 Free PMC article.
-
A novel approach for engineering DHCM/GelMA microgels: application in hepatocellular carcinoma cell encapsulation and chemoresistance research.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Mar 14;13:1564543. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1564543. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40161518 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated multi-omic analysis and experiment reveals the role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in lung adenocarcinoma.BMC Med Genomics. 2024 Jan 2;17(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12920-023-01785-4. BMC Med Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38167084 Free PMC article.
-
ARHGAP18 is Upregulated by Transcription Factor GATA1 Promotes the Proliferation and Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024 Feb;196(2):679-689. doi: 10.1007/s12010-023-04459-0. Epub 2023 May 12. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37171759
-
Myriad factors and pathways influencing tumor radiotherapy resistance.Open Life Sci. 2024 Nov 26;19(1):20220992. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0992. eCollection 2024. Open Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39655194 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. - PubMed
-
- Ursino S, Greco C, Cartei F, Colosimo C, Stefanelli A, Cacopardo B, Berretta M, Fiorica F. Radiotherapy and hepatocellular carcinoma: update and review of the literature. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2012;16(11):1599–1604. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

