The efficacy of minocycline hydrochloride ointment versus iodoform gauze for alveolar osteitis: A prospective cohort study
- PMID: 36258229
- PMCID: PMC9580180
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-022-02468-9
The efficacy of minocycline hydrochloride ointment versus iodoform gauze for alveolar osteitis: A prospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Alveolar osteitis (AO) is one of the most commonly encountered complication following tooth extraction, however, to date there is no standard methods of prevention and treatment. The study aims to investigate the efficiency of minocycline hydrochloride ointment (MHO) for the treatment of alveolar osteitis compared with traditional treatment with iodoform gauze (IG).
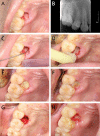
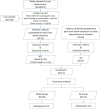
Methods/design: STROBE checklist was followed to report this study. All patients underwent tooth extraction either in our department or other hospitals, whom presented with postoperative pain, were screened out to meet the inclusion and exclusion criteria of this study about AO. Patients who fulfilled the inclusion criteria were enrolled in our prospective cohort study, and MHO or IG was administered. The Visual analog scale scores were used to assess the pain score of patients. The healing status of the extraction sockets was followed up. Differences in responses between groups were analyzed using Mann-Whitney U tests. Chi-square test was performed to explore the differences in the teeth position of AO.
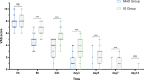
Results: Of 41,371 patients underwent tooth extraction with post-operative follow-up in our departments, only 20 patients (0.05%) suffered from AO. 31 patients with AO, whose teeth were extracted in other places, were also enrolled. The incidence of AO was significantly higher in third molars than other teeth (P < 0.01). In 28 patients that were treated with MHO, the pain was relieved substantially on day 3 and almost painless on day 7. And only 25% of cases required dressing change more than once. Whilst 23 patients treated with IG, the pain was relieved on day 5, and 56.5% of cases required multiple dressing change. The difference between the two groups of VAS scores had statistical significance during treatment at 8 h, 24 h, 3d, 5d, and 7d. No allergic reaction or further infection occurred.
Conclusion: MHO has a safer and higher therapeutic effect in the treatment of AO compared with traditional treatment with IG. MHO may become a preferred treatment modality for AO.
Keywords: Alveolar osteitis; Iodoform gauze; Minocycline; Therapeutics.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Influence of immediate post-extraction socket irrigation on development of alveolar osteitis after mandibular third molar removal: a prospective split-mouth study, preliminary report.Br Dent J. 2012 Dec;213(12):597-601. doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.2012.1134. Br Dent J. 2012. PMID: 23257808
-
Effects of the topical hemostatic agent Ankaferd Blood Stopper on the incidence of alveolar osteitis after surgical removal of an impacted mandibular third molar.Niger J Clin Pract. 2014 Jan-Feb;17(1):75-80. doi: 10.4103/1119-3077.122847. Niger J Clin Pract. 2014. PMID: 24326812 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of oral contraceptives on the prevalence of alveolar osteitis after mandibular third molar surgery: a retrospective study.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016 Oct;45(10):1299-302. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2016.05.022. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016. PMID: 27312101
-
Surgical techniques for the removal of mandibular wisdom teeth.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 26;7(7):CD004345. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004345.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32712962 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of platelet-rich fibrin on mandibular third molar surgery recovery: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Oral Health. 2019 Jul 25;19(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s12903-019-0824-3. BMC Oral Health. 2019. PMID: 31345203 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Use of Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF) in the Management of Dry Socket: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 19;25(18):10069. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810069. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337554 Free PMC article.
-
Minocycline hydrochloride ointment combined with Vitapex paste is effective for middle-aged and elderly patients with combined periodontal-endodontic lesions.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Jan 15;16(1):314-322. doi: 10.62347/NLWG5751. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38322572 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

