The Promise of Artificial Intelligence in Cardiothoracic Surgery
- PMID: 36258643
- PMCID: PMC9733411
- DOI: 10.5090/jcs.22.083
The Promise of Artificial Intelligence in Cardiothoracic Surgery
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
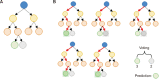
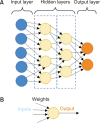
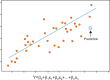
References
-
- Rajkomar A, Kannan A, Chen K, et al. Automatically charting symptoms from patient-physician conversations using machine learning. JAMA Intern Med. 2019;179:836–8. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.8558. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.8558. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nilsson J, Ohlsson M, Thulin L, Hoglund P, Nashef SA, Brandt J. Risk factor identification and mortality prediction in cardiac surgery using artificial neural networks. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006;132:12–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2005.12.055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2005.12.055. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Christodoulou E, Ma J, Collins GS, Steyerberg EW, Verbakel JY, Van Calster B. A systematic review shows no performance benefit of machine learning over logistic regression for clinical prediction models. J Clin Epidemiol. 2019;110:12–22. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2019.02.004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2019.02.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ranucci M, Johnson I, Willcox T, et al. Goal-directed perfusion to reduce acute kidney injury: a randomized trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2018;156:1918–27. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2018.04.045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2018.04.045. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Andras I, Mazzone E, van Leeuwen FW, et al. Artificial intelligence and robotics: a combination that is changing the operating room. World J Urol. 2020;38:2359–66. doi: 10.1007/s00345-019-03037-6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-019-03037-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

