Chlorogenic acid alleviates the reduction of Akt and Bad phosphorylation and of phospho-Bad and 14-3-3 binding in an animal model of stroke
- PMID: 36259103
- PMCID: PMC9715392
- DOI: 10.4142/jvs.22200
Chlorogenic acid alleviates the reduction of Akt and Bad phosphorylation and of phospho-Bad and 14-3-3 binding in an animal model of stroke
Abstract
Background: Stroke is caused by disruption of blood supply and results in permanent disabilities as well as death. Chlorogenic acid is a phenolic compound found in various fruits and coffee and exerts antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic effects.
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to investigate whether chlorogenic acid regulates the PI3K-Akt-Bad signaling pathway in middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO)-induced damage.
Methods: Chlorogenic acid (30 mg/kg) or vehicle was administered peritoneally to adult male rats 2 h after MCAO surgery, and animals were sacrificed 24 h after MCAO surgery. Neurobehavioral tests were performed, and brain tissues were isolated. The cerebral cortex was collected for Western blot and immunoprecipitation analyses.
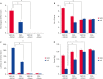
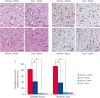
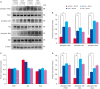
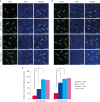
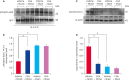
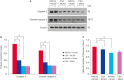
Results: MCAO damage caused severe neurobehavioral disorders and chlorogenic acid improved the neurological disorders. Chlorogenic acid alleviated the MCAO-induced histopathological changes and decreased the number of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling-positive cells. Furthermore, MCAO-induced damage reduced the expression of phospho-PDK1, phospho-Akt, and phospho-Bad, which was alleviated with administration of chlorogenic acid. The interaction between phospho-Bad and 14-3-3 levels was reduced in MCAO animals, which was attenuated by chlorogenic acid treatment. In addition, chlorogenic acid alleviated the increase of cytochrome c and caspase-3 expression caused by MCAO damage.
Conclusions: The results of the present study showed that chlorogenic acid activates phospho-Akt and phospho-Bad and promotes the interaction between phospho-Bad and 14-3-3 during MCAO damage. In conclusion, chlorogenic acid exerts neuroprotective effects by activating the Akt-Bad signaling pathway and maintaining the interaction between phospho-Bad and 14-3-3 in ischemic stroke model.
Keywords: Chlorogenic acid; ischemic stroke; neuroprotection.
© 2022 The Korean Society of Veterinary Science.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ingall T. Stroke--incidence, mortality, morbidity and risk. J Insur Med. 2004;36(2):143–152. - PubMed
-
- Grysiewicz RA, Thomas K, Pandey DK. Epidemiology of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke: incidence, prevalence, mortality, and risk factors. Neurol Clin. 2008;26(4):871–895. - PubMed
-
- Khoshnam SE, Winlow W, Farzaneh M, Farbood Y, Moghaddam HF. Pathogenic mechanisms following ischemic stroke. Neurol Sci. 2017;38(7):1167–1186. - PubMed
-
- Broughton BR, Reutens DC, Sobey CG. Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 2009;40(5):e331–e339. - PubMed
-
- Chan PH. Mitochondria and neuronal death/survival signaling pathways in cerebral ischemia. Neurochem Res. 2004;29(11):1943–1949. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

