Cabozantinib for previously treated radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer: Updated results from the phase 3 COSMIC-311 trial
- PMID: 36259380
- PMCID: PMC10092751
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.34493
Cabozantinib for previously treated radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer: Updated results from the phase 3 COSMIC-311 trial
Erratum in
-
Erratum to "Cabozantinib for previously treated radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer: Updated results from the phase 3 COSMIC-311 trial".Cancer. 2023 Mar 1;129(5):807. doi: 10.1002/cncr.34638. Epub 2023 Jan 13. Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36637398 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: At an interim analysis (median follow-up, 6.2 months; n = 187), the phase 3 COSMIC-311 trial met the primary end point of progression-free survival (PFS): cabozantinib improved PFS versus a placebo (median, not reached vs. 1.9 months; p < .0001) in patients with previously treated radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer (RAIR-DTC). The results from an exploratory analysis using an extended datacut are presented.
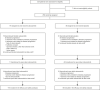
Methods: Patients 16 years old or older with RAIR-DTC who progressed on prior lenvatinib and/or sorafenib were randomized 2:1 to oral cabozantinib tablets (60 mg/day) or a placebo. Placebo patients could cross over to open-label cabozantinib upon radiographic disease progression. The objective response rate (ORR) in the first 100 randomized patients and the PFS in the intent-to-treat population, both according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors version 1.1 by blinded, independent review, were the primary end points.
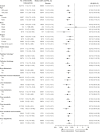
Results: At the data cutoff (February 8, 2021), 258 patients had been randomized (cabozantinib, n = 170; placebo, n = 88); the median follow-up was 10.1 months. The median PFS was 11.0 months (96% confidence interval [CI], 7.4-13.8 months) for cabozantinib and 1.9 months (96% CI, 1.9-3.7 months) for the placebo (hazard ratio, 0.22; 96% CI, 0.15-0.32; p < .0001). The ORR was 11.0% (95% CI, 6.9%-16.9%) versus 0% (95% CI, 0.0%-4.1%) (p = .0003) with one complete response with cabozantinib. Forty placebo patients crossed over to open-label cabozantinib. Grade 3/4 treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 62% and 28% of the cabozantinib- and placebo-treated patients, respectively; the most common were hypertension (12% vs. 2%), palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (10% vs. 0%), and fatigue (9% vs. 0%). There were no grade 5 treatment-related events.
Conclusions: At extended follow-up, cabozantinib maintained superior efficacy over a placebo in patients with previously treated RAIR-DTC with no new safety signals.
Keywords: COSMIC-311; cabozantinib; differentiated thyroid cancer; phase 3; placebo; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
© 2022 The Authors. Cancer published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Cancer Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Marcia S. Brose has received honoraria from Bayer, Eisai, and Lilly; has a consulting or advisory role with Bayer, Blueprint Medicines, Eisai, Exelixis, Lilly, and Loxo; and has received institutional research funding from Bayer, Blueprint Medicines, Eisai, Exelixis, Lilly, and Loxo. Bruce G. Robinson has leadership roles with Cochlear and Mayne Pharma; has stock and other ownership interests in Cochlear and Mayne Pharma; has a consulting or advisory role with Eisai and Loxo; has participated in speakers’ bureaus with Eisai; and has received travel support, accommodations, or other expenses from Eisai. Steven I. Sherman has received honoraria from Eisai; has a consulting or advisory role with Exelixis, Lilly, and Loxo; and has received institutional research funding from Exelixis. Barbara Jarzab has received honoraria from Sanofi; has a consulting or advisory role with AstraZeneca, Ewopharma, and Ipsen; has participated in speakers’ bureaus with Exelixis; has acted as an independent contractor for Amgen, Eisai, Pfizer, Lilly, Sobi, and Oxigene; and has received travel support, accommodations, or other expenses from Edomed, Ipsen, Novartis, Bayer, Sobi, and Sanofi. Chia‐Chi Lin has received honoraria from Daiichi Sankyo, Lilly, Novartis, and Roche; has a consulting or advisory role with Blueprint Medicines, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi Sankyo, and Novartis; has acted as an independent contractor for Bristol‐Myers Squibb, EMD Serono, BeiGene, and AbbVie; and has received travel support, accommodations, or other expenses from BeiGene, Daiichi Sankyo, Lilly, and Novartis. Fernanda Vaisman has a consulting or advisory role with Bayer HealthCare and Merck. Ana O. Hoff has received honoraria from Bayer (continuing medical education), Genzyme (continuing medical education), and United (continuing medical education); has a consulting or advisory role with Exelixis, Lilly, and Bayer; and has received institutional research funding from Exelixis and Lilly. Daniel W. Bowles has a consulting or advisory role with Exelixis. Suvajit Sen is an employee of Exelixis and has stock and other ownership interests with Exelixis. Jennifer W. Oliver is an employee of Exelixis and has stock and other ownership interests with Exelixis. Kamalika Mukherjee is an employee of Exelixis and has stock and other ownership interests with Exelixis. Bhumsuk Keam has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Merck, and MSD Oncology; has a consulting or advisory role with ABL Bio, AstraZeneca, CbsBioscience, Cellid, Genexine, Handok, and MSD Oncology; and has received research funding from AstraZeneca, MSD Oncology, and Ono Pharmaceutical. Jaume Capdevila has a consulting or advisory role with Advanced Accelerator Applications, Bayer, Eisai, Exelixis, Ipsen, Lilly, Merck Serono, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Vall Hebron; has participated in speakers’ bureaus with Bayer, Eisai, Ipsen, Lilly, Merck Serono, Novartis, Pfizer, and Sanofi; and has received institutional research funding from Advanced Accelerator Applications, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Eisai, Ipsen, Lilly, Novartis, and Pfizer. The other authors made no disclosures.
Figures

References
-
- Brose MS, Schlumbeger M, Jeffers M, Kappeler C, Meinhardt G, Pena CEA. Analysis of biomarkers and association with clinical outcomes in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer: subanalysis of the sorafenib phase III DECISION trial. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25(24):7370‐7380. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-18-3439 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

